Resistin (human) ELISA Kit
Product Code:
AG-45A-0023Y
AG-45A-0023Y
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Target Species:
Human
Human
Application:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Shipping:
BLUE ICE
BLUE ICE
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: +4°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: +4°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-45A-0023YEK-KI01 | 96 wells | £430.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
FIZZ3; Found in Inflammatory Zone 3; ADSF; Adipose Tissue-Specific Secretory Factor
Assay Type:
Sandwich
Detection Type:
Colorimetric
EClass:
32160000
Handling Advice:
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use.
Long Description:
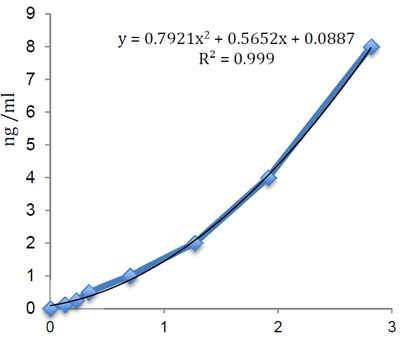
ELISA Assay. Detects human resistin. Does not cross-react with mouse resistin, rat resistin, human RELM-beta, mouse RELM-alpha, mouse RELM-beta, rat RELM-alpha, human leptin or human adiponectin. Colorimetric assay. Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum. Range: 0.125 to 8ng/ml. Sensitivity: 100pg/ml. Resistin (FIZZ3; ADSF; Adipose tissue-specific secretory factor) is a 12.5kDa cysteine-rich adipocytokine. In rodents, increased resistin-levels impair insulin action, while genetic ablation or down-regulation of the resistin gene improves insulin sensitivity. In humans most reports identified inflammatory cells and bone marrow-derived cells as the main source of resistin, indicating a role in inflammatory responses. Plasma resistin levels were shown to be associated with C-reactive protein (CRP), inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn?s disease, atherosclerosis and acute pancreatitis. Atherosclerosis and obesity are increasingly viewed as chronic inflammatory conditions. Circulating resistin levels were reported to be increased in obesity and diabetes.
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
Q9HD89
Package Type:
Box
Product Description:
Resistin (FIZZ3; ADSF; Adipose tissue-specific secretory factor) is a 12.5kDa cysteine-rich adipocytokine. In rodents, increased resistin-levels impair insulin action, while genetic ablation or down-regulation of the resistin gene improves insulin sensitivity. In humans most reports identified inflammatory cells and bone marrow-derived cells as the main source of resistin, indicating a role in inflammatory responses. Plasma resistin levels were shown to be associated with C-reactive protein (CRP), inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn?s disease, atherosclerosis and acute pancreatitis. Atherosclerosis and obesity are increasingly viewed as chronic inflammatory conditions. Circulating resistin levels were reported to be increased in obesity and diabetes.
Range:
0.125 to 8ng/ml
Sample Type:
Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum
Sensitivity:
100pg/ml
Specificity:
Detects human resistin. Does not cross-react with mouse resistin, rat resistin, human RELM-beta, mouse RELM-alpha, mouse RELM-beta, rat RELM-alpha, human leptin or human adiponectin.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
ELISA Kits
UNSPSC Number:
41116126
Use & Stability:
12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box.
References
Plasma resistin concentrations measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a newly developed monoclonal antibody are elevated in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: B.S. Youn, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 150 (2004) | Common genetic polymorphisms in the promoter of resistin gene are major determinants of plasma resistin concentrations in humans: Y.M. Cho, et al.; Diabetologia 47, 559 (2004) | Correlations between umbilical and maternal serum resistin levels and neonatal birth weight: Cho GJ, et al.; Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 85, 1051 (2006) | Relationship of serum adiponectin and resistin levels with breast cancer risk: J.H. Kang, et al.; J. Korean Med. Sci. 22, 117 (2007) | Leptin is Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Healthy Obese Premenopausal Women: K. Kwon, et al.; Kor. Circ. J. 37, 251 (2007) | Correlation between estrogens and serum adipocytokines in premenopausal and postmenopausal women: S.C. Hong, et al.; Menopause 14, 835 (2007) | Association of adiponectin and resistin with cardiovascular events in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean atherosclerosis study (KAS): A 42-month prospective study: S. Lim, et al.; Atherosclerosis 196, 398 (2008) | Adipokines and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Relationship with Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: M. Vadacca, et al.; J. Rheumatol. 36, 295 (2009) | Relationship between serum adipocytokine levels and metabolic syndrome in menopausal women: H.T. Park, et al.; Gynecol. Endocrinol. 25, 27 (2009) | A 12-week regimen of caloric restriction improves levels of adipokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines in Korean women with BMIs greater than 23 kg/m2: I.S. Lee, et al.; Inflamm. Res. 59, 399 (2010) | Alteration of adipokines during peripheral blood stem cell mobilization induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: Y. Tanaka, et al.; J. Clin. Apheresis 24, 205 (2009) | Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and their association with plasma levels of resistin and the metabolic syndrome in a South Indian population: A. Haseeb, et al.; J. Biosci. 34, 405 (2009) | Reconsideration of insulin signals induced by improved laboratory animal diets, Japanese and American diets, in IRS-2 deficient mice: H. Hashimoto, et al.; Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. 117, 577 (2009) | Comparison of serum levels and the placental expression of resistin between patients with preeclampsia and normal pregnant women: H.J. Seol, et al.; Hypertens. Pregnancy. 29, 310 (2010) | Association of adiponectin, resistin, and vascular inflammation: analysis with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography: H.Y. Choi, et al.; Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31, 944 (2011) | Expression of resistin in the prostate and its stimulatory effect on prostate cancer cell proliferation; H.J. Kim, et al.; BJU Int. 108, E77 (2011) | Occurrence of Buffalo Hump and Laryngeal Cancer in a HIV-1 Infected Patient with Metabolic Disorders Receiving a Rescue HAART Regimen: A. Fantauzzi, et al.; J. Med. Cases 3, 185 (2012) | Therapeutic Lifestyle Modification Program Reduces Plasma Levels of the Chemokines CRP and MCP-1 in Subjects With Metabolic Syndrome: E.G. Oh, et al.; Biol. Res. Nurs. 15, 48 (2013) | Human resistin, a proinflammatory cytokine, shows chaperone-like activity: M. Suragani, et al.; PNAS 110, 20467 (2013) | Identification of adipokine clusters related to parameters of fat mass, insulin sensitivity and inflammation: G. Flehmig, et al.; PLoS One 9, e99785 (2014) | Associations of a Panel of Adipokines with Fat Deposits and Metabolic Phenotypes in a General Population: J. Fischer, et al.; Obesity 28, 1550 (2020) | Metabolic syndrome and adipokine levels in systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis: A. Gigante, et al.; Clin. Rheumatol. 40, 4253 (2021)