VEGFR-1, Soluble (human) (rec.)
Product Code:
AG-40T-0049
AG-40T-0049
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Target Species:
Human
Human
Shipping:
Blue Ice
Blue Ice
Storage:
+4°C
+4°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-40T-0049-C005 | 5 ug | £155.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-40T-0049-C020 | 20 ug | £280.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1; FLT-1; Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase 1
Biological Activity:
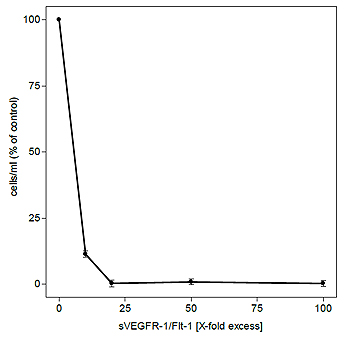
The activity of sVEGFR-1 was determined by its ability to inhibit the VEGF-A-induced proliferation of HUVECs.
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Lyophilized.
Handling Advice:
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution.
Long Description:
Protein. Human sVEGFR-1 (663aa). Source: Sf9 cells. Lyophilized. Purity: >95% (SDS-PAGE). Recombinant human soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1) is the naturally occurring form and is a glycosylated monomeric protein. The biological function of sVEGFR-1 seems to be an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis, binding VEGF with the same affinity as the full-length receptor. VEGFR-1 is a tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis and cancer cell invasion. It may play an essential role as a negative regulator of embryonic angiogenesis by inhibiting excessive proliferation of endothelial cells. It can promote endothelial cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis in adulthood. Its function in promoting cell proliferation seems to be cell-type specific. Promotes PGF-mediated proliferation of endothelial cells, proliferation of some types of cancer cells, but does not promote proliferation of normal fibroblasts (in vitro). It has a very high affinity for VEGFA and relatively low protein kinase activity. It may function as a negative regulator of VEGFA signaling by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and preventing its binding to KDR. Modulates KDR signaling by forming heterodimers with KDR. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of phospholipase C-gamma (PLCG) leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leading to activation of phosphatidylinositol kinase and the downstream signaling pathway. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates SRC and YES1 and may also phosphorylate CBL.
Molecular Weight:
~96kDa (monomer)
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
P17948-2
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Recombinant human soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1) is the naturally occurring form and is a glycosylated monomeric protein. The biological function of sVEGFR-1 seems to be an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis, binding VEGF with the same affinity as the full-length receptor. VEGFR-1 is a tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis and cancer cell invasion. It may play an essential role as a negative regulator of embryonic angiogenesis by inhibiting excessive proliferation of endothelial cells. It can promote endothelial cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis in adulthood. Its function in promoting cell proliferation seems to be cell-type specific. Promotes PGF-mediated proliferation of endothelial cells, proliferation of some types of cancer cells, but does not promote proliferation of normal fibroblasts (in vitro). It has a very high affinity for VEGFA and relatively low protein kinase activity. It may function as a negative regulator of VEGFA signaling by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and preventing its binding to KDR. Modulates KDR signaling by forming heterodimers with KDR. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of phospholipase C-gamma (PLCG) leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leading to activation of phosphatidylinositol kinase and the downstream signaling pathway. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates SRC and YES1 and may also phosphorylate CBL.
Purity:
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Sequence:
Human sVEGFR-1 (661aa).
Source / Host:
Sf9 cells
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Other Proteins
UNSPSC Number:
12352202
Use & Stability:
After reconstitution, store at -80°C. Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Soluble VEGFR-1 secreted by endothelial cells and monocytes is present in human serum and plasma from healthy donors: B. Barleon, et al.; Angiogenesis 4, 143 (2001) | Poor responder-high responder: the importance of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 in ovarian stimulation protocols: J. Neulen, et al.; Human Reprod. 16, 621 (2001) | Activation of Vascular Endothelial Growth FactorReceptor-1 Sustains Angiogenesis and Bcl-2 ExpressionVia the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway in Endothelial Cells: J. Cai, et al.; Diabetes 52, 2959 (2003) | Elevated Placental Soluble Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 Inhibits Angiogenesis in Preeclampsia: S. Ahmad & A. Ahmed; Circ. Res. 95, 884 (2004) | Autocrine activity of soluble Flt-1 controls endothelial cell function and angiogenesis: S. Ahmad, et al.; Vasc. Cell 3, 15 (2011) | The role of heterodimerization between VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in the regulation of endothelial cell homeostasis: MJ. Cudmore, et al.; Nat. Commun. 3, 972 (2012) | Altered redox state modulates endothelial KCa2.3 and KCa3.1 levels in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia: S. Choi, et al.; Antioxid. Redox. Signal 30, 505 (2019)