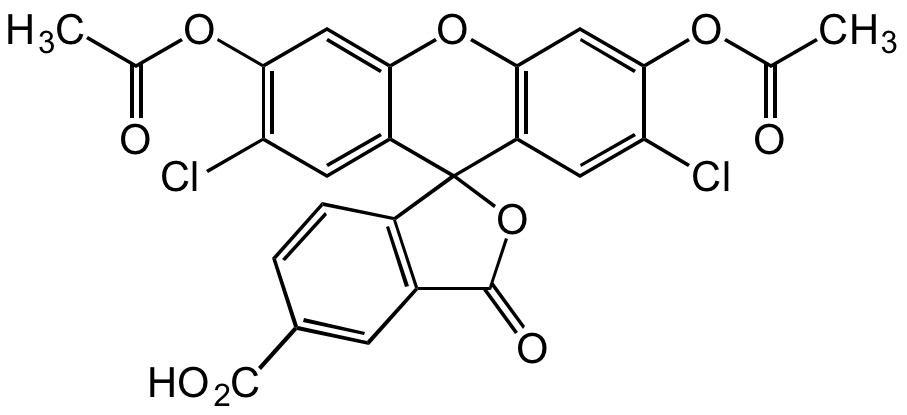
5-Carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein DA
Product Code:
CDX-C0333
CDX-C0333
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
-20 °C
-20 °C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0333-M100 | 100 mg | £230.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-C0333-M250 | 250 mg | £450.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
5-CDCFDA; 5-Carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate; 5-Carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein DA
Appearance:
Off-white powder.
CAS:
144489-09-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C25H14Cl2O9/c1-10(28)33-21-8-19-15(6-17(21)26)25(14-4-3-12(23(30)31)5-13(14)24(32)36-25)16-7-18(27)22(34-11(2)29)9-20(16)35-19/h3-9H,1-2H3,(H,30,31)
InChiKey:
AJIVVDSJIOOZOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 144489-09-8. Formula: C25H14Cl2O9. MW: 529.28. Synthetic. Non-activated, amine-reactive fluorescent probe. Single 5-isomer of CDCFDA that can be used in biomolecules conjugation. CDCFDA is an amine?reactive fluorescein diacetate (FDA) derivative used to prepare a variety of FDA conjugates. CDCFDA is a non-fluorescent molecule that diffuse into cells and is hydrolyzed by intracellular non-specific esterases, yielding a fluorescent probe. The probe accumulates exclusively in viable cells with intact cell membranes. CFCFDA does not stain dead cells. CDCFDA labeling can be used for monitoring cells by flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy. The probe is also frequently used to monitor reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in live cells and intracellular pH levels. Spectral data: lambdaex=504nm, lambdaem=529nm.
MDL:
MFCD00037454
Molecular Formula:
C25H14Cl2O9
Molecular Weight:
529.28
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Non-activated, amine-reactive fluorescent probe. Single 5-isomer of CDCFDA that can be used in biomolecules conjugation. CDCFDA is an amine?reactive fluorescein diacetate (FDA) derivative used to prepare a variety of FDA conjugates. CDCFDA is a non-fluorescent molecule that diffuse into cells and is hydrolyzed by intracellular non-specific esterases, yielding a fluorescent probe. The probe accumulates exclusively in viable cells with intact cell membranes. CFCFDA does not stain dead cells. CDCFDA labeling can be used for monitoring cells by flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy. The probe is also frequently used to monitor reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in live cells and intracellular pH levels. Spectral data: lambdaex=504nm, lambdaem=529nm.
Purity:
>95% (NMR)
SMILES:
ClC1=C(OC(C)=O)C=C2C(C3(C(C=CC(C(O)=O)=C4)=C4C(O3)=O)C(C=C(Cl)C(OC(C)=O)=C5)=C5O2)=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, DMF, acetonitrile, methanol or chloroform.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Fluorescent Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
(1) C.K. Raymond et al.; J. Cell Biol. 111, 877 (1990) | (2) J.P. Kehrer & T. Paraidathathu; Free Rad. Res. Commun. 16, 217 (1992) | (3) Q.P. Lloyd, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 270, 22445 (1995) | (4) A.L. Inselman, et al.; Curr. Microbiol. 38, 295 (1999) | (5) M.J. Zamek-Gliszczynski, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 304, 801 (2003) | (6) L. Li, et al.; Free Radic. Res. 42, 354 (2008) | (7) M. Medhora, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 294, L902 (2008) | (8) S. Siissalo, et al.; Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 71, 332 (2009) | (9) A.I. Pogue, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 9615 (2012) | (10) J. Roh, et al.; Redox Biol. 11, 254 (2016) | (11) J.L. Roh, et al.; Cancer Lett. 381, 96 (2016)