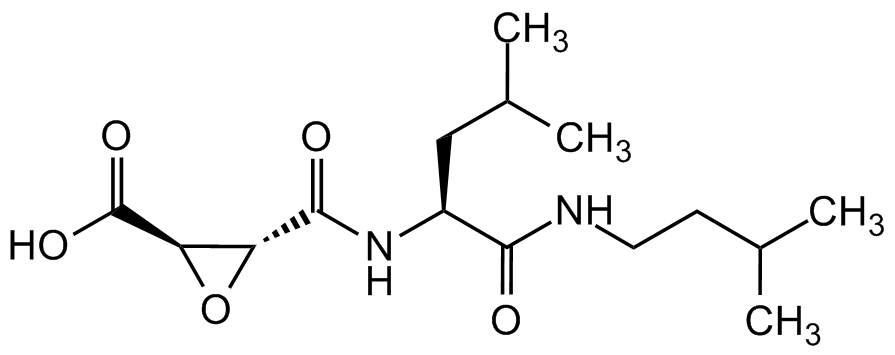
Loxistatin acid [E-64c]
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CP3-7007-M001 | 1 mg | £70.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CP3-7007-M005 | 5 mg | £250.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term Storage: +4?C. Long Term Storage: -20?C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Ep 475; 2S,3S-trans-(Carboxyoxirane-2-carbonyl)-L-leucine-(3-methylbutyl) amide; NSC 694279
Appearance:
White solid.
CAS:
76684-89-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C15H26N2O5/c1-8(2)5-6-16-13(18)10(7-9(3)4)17-14(19)11-12(22-11)15(20)21/h8-12H,5-7H2,1-4H3,(H,16,18)(H,17,19)(H,20,21)/t10-,11+,12+/m0/s1
InChiKey:
SCMSYZJDIQPSDI-QJPTWQEYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 76684-89-4. Formula: C15H26N2O5. Molecular Weight: 314.4. E-64c is a potent cell-impermeable epoxysuccinyl peptide inhibitor of calpain and other cysteine proteases, such as papain, cathepsin B, H and L. Does not inhibit the serine proteases trypsin, chymotrypsin or elastase. E-64c is an active metabolite of the protease inhibitor E-64d (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3737), and a synthetic analog of E-64 (Prod. No. AG-CP3-7006). Studies indicate that E-64c is a more potent inhibitor of cathepsins B and L compared to E-64. E-64c has in vitro antiviral, antiparasitic and immunomodulatory properties. It reduces the autocatalytic activity of the foot-and-mouth-disease virus (FMDV) leader protease, reduces infection of HEK293T cells by an HIV-based virus system pseudotyped with SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein in a concentration-dependent manner, inhibits human rotavirus replication, and exhibits entry-blocking effects against MERS-CoV. It also inhibits the trypanosomal cysteine protease cruzain. Significantly reduces calpain-mediated depletion of microtubule-associated protein (MAP2) in an animal model of an ischemic brain.
MDL:
MFCD00132882
Molecular Formula:
C15H26N2O5
Molecular Weight:
314.4
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
E-64c is a potent cell-impermeable epoxysuccinyl peptide inhibitor of calpain and other cysteine proteases, such as papain, cathepsin B, H and L. Does not inhibit the serine proteases trypsin, chymotrypsin or elastase. E-64c is an active metabolite of the protease inhibitor E-64d (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3737), and a synthetic analog of E-64 (Prod. No. AG-CP3-7006). Studies indicate that E-64c is a more potent inhibitor of cathepsins B and L compared to E-64. E-64c has in vitro antiviral, antiparasitic and immunomodulatory properties. It reduces the autocatalytic activity of the foot-and-mouth-disease virus (FMDV) leader protease, reduces infection of HEK293T cells by an HIV-based virus system pseudotyped with SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein in a concentration-dependent manner, inhibits human rotavirus replication, and exhibits entry-blocking effects against MERS-CoV. It also inhibits the trypanosomal cysteine protease cruzain. Significantly reduces calpain-mediated depletion of microtubule-associated protein (MAP2) in an animal model of an ischemic brain.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
O=C(O)[C@H]1[C@H](C(N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(NCCC(C)C)=O)=O)O1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or ethanol (10mg/ml). Slightly soluble in water (1mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20?C.
References
The effect of an in vivo-injected thiol protease inhibitor, E-64-c, on the calcium-induced degeneration of myofilaments: S. Ishiura, et al.; J. Biochem. 90, 1557 (1981) | L-trans-Epoxysuccinyl-leucylamido(4-guanidino)butane (E-64) and its analogues as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases including cathepsins B, H and L: A.J. Barrett, et al.; Biochem. J. 201, 189 (1982) | In vitro and in vivo inhibition of cysteine proteinases by EST, a new analog of E-64: M. Tamai, et al.; J. Pharmacobiodyn. 9, 672 (1986) | Mode of binding of E-64-c, a potent thiol protease inhibitor, to papain as determined by X-ray crystal analysis of the complex: K. Matsumoto, et al.; FEBS Lett. 245, 177 (1989) | Calcium-activated neutral protease inhibitor (E-64c) and reperfusion for experimental myocardial infarction: G. Toda, et al.; Jpn. Heart J. 30, 375 (1989) | Protease inhibitors prevent the development of human rotavirus-induced diarrhea in suckling mice: T. Ebina & K. Tsukada; Microbiol. Immunol. 35, 583 (1991) | Antiviral effects of a thiol protease inhibitor on foot-and-mouth disease virus: L.G. Kleina & M.J. Grubman; J. Virol. 66, 7168 (1992) | Structural basis of inhibition of cysteine proteases by E-64 and its derivatives: K. Matsumoto, et al.; Pept. Sci. 51, 99 (1999) | Design, synthesis and evaluation of d-homophenylalanyl epoxysuccinate inhibitors of the trypanosomal cysteine protease cruzain: W.R. Roush, et al.; Tetrahedron 56, 9747 (2000) | Inhibitors of cathepsin L prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry: G. Simmons, et al.; PNAS 102, 11876 (2005) | Safe, High-Throughput Screening of Natural Compounds of MERS-CoV Entry Inhibitors Using a Pseudovirus Expressing MERS-CoV Spike Protein: J.Y. Kim, et al.; Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 52, 730 (2018)