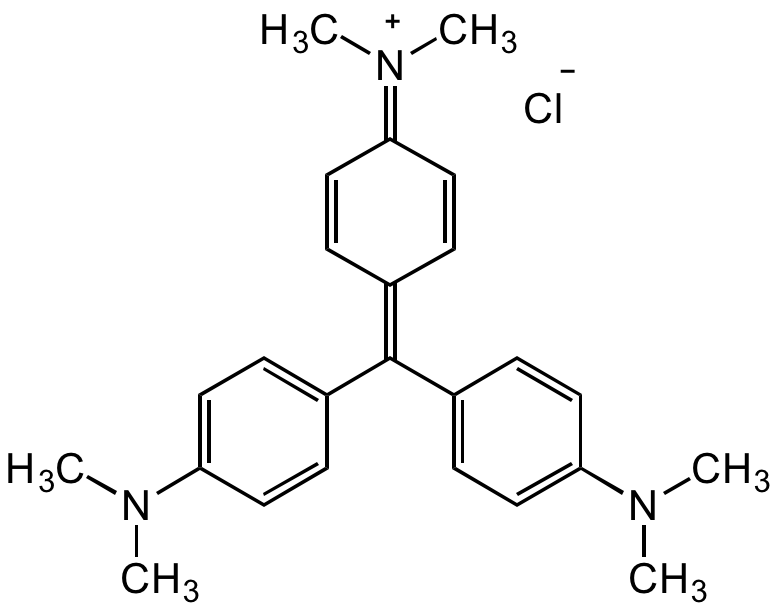
Crystal Violet
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0252-G025 | 25 g | £41.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-C0252-G100 | 100 g | £108.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Basic Violet 3; Gentian Violet; Hexamethylpararosaniline chloride; Methyl Violet 10B; C.I. 42555
Appearance:
Dark green powder.
CAS:
548-62-9
Class:
9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS05,GHS07,GHS09
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302, H318, H351, H410
InChi:
InChI=1S/C25H30N3.ClH/c1-26(2)22-13-7-19(8-14-22)25(20-9-15-23(16-10-20)27(3)4)21-11-17-24(18-12-21)28(5)6;/h7-18H,1-6H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
InChiKey:
ZXJXZNDDNMQXFV-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 548-62-9. Formula: C25H30N3Cl. MW: 407.98. Crystal Violet is used as an acid-base indicator. When dissolved in water, the dye has a blue-violet colour with an absorbance maximum at 590nm and an extinction coefficient of 87,000 M-1 cm-1. The colour of the dye depends on the acidity of the solution. At a pH of >1.0, the dye is green with absorption maxima at 420nm and 620nm, while in a strongly acidic solution the dye is yellow with an absorption maximum at 420nm. Spectral data: UV/Visible Absorbance: lambda max (water) 584-590nm. Crystal violet is used as an active component, primary stain, of Gram stain for differentiation of Gram-negative versus Gram-positive bacteria. It has been used to check cell viability, for the staining of cells to study cell migration, invasion and cell viability and as a nontoxic DNA stain for DNA visualization in agarose gels. Solutions containing crystal violet and formalin are often used to simultaneously fix and stain cells grown in tissue culture to preserve them and make them easily visible, since most cells are colourless. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antifungal, antihelminthic, antitrypanosomal, antiangiogenic, and antitumor properties. It has shown to calcium-dependent uncouple oxidative phosphorylation. It is used to dye paper, as a component of navy blue and black inks, ball-point pens and inkjet printers. It is also used to colourize diverse products such as fertilizers, antifreezes and detergents. In forensics, gentian violet was used to develop fingerprints.
MDL:
MFCD00011750
Molecular Formula:
C25H30N3Cl
Molecular Weight:
407.98
Package Type:
Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P501
Product Description:
Crystal Violet is used as an acid-base indicator. When dissolved in water, the dye has a blue-violet colour with an absorbance maximum at 590nm and an extinction coefficient of 87,000 M-1 cm-1. The colour of the dye depends on the acidity of the solution. At a pH of >1.0, the dye is green with absorption maxima at 420nm and 620nm, while in a strongly acidic solution the dye is yellow with an absorption maximum at 420nm. Spectral data: UV/Visible Absorbance: lambda max (water) 584-590nm. Crystal violet is used as an active component, primary stain, of Gram stain for differentiation of Gram-negative versus Gram-positive bacteria. It has been used to check cell viability, for the staining of cells to study cell migration, invasion and cell viability and as a nontoxic DNA stain for DNA visualization in agarose gels. Solutions containing crystal violet and formalin are often used to simultaneously fix and stain cells grown in tissue culture to preserve them and make them easily visible, since most cells are colourless. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antifungal, antihelminthic, antitrypanosomal, antiangiogenic, and antitumor properties. It has shown to calcium-dependent uncouple oxidative phosphorylation. It is used to dye paper, as a component of navy blue and black inks, ball-point pens and inkjet printers. It is also used to colourize diverse products such as fertilizers, antifreezes and detergents. In forensics, gentian violet was used to develop fingerprints.
Purity:
>88% (dye content)
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
CN(C)C1=CC=C(/C(C2=CC=C(N(C)C)C=C2)=C3C=C/C(C=C/3)=[N+](C)/C)C=C1.[Cl-]
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
3077
UNSPSC Category:
Fluorescent Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) E.Q. Adams & L. Rosenstein; JACS 36, 1452 (1914) | (2) C.E. Hoffmann & O. Rahn; J. Bacteriol. 47, 177 (1944) | (3) H.L. Chance; Stain Technol. 27, 253 (1952) | (4) W.H. Clarke & I.G. Maddocks; Stain Technol. 38, 252 (1963) | (5) M.K. Tolba & A.M. Saleh; Arch. Mikrobiol. 47, 201 (1963) | (6) E. Adams; Stain Technol. 50, 227 (1975) | (7) W. Au, et al.; Mutat. Res. 58, 269 (1978) | (8) L.P. Wakelin, et al.; Biochemistry 20, 5779 (1981) | (9) S.N. Moreno, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 263, 12493 (1988) | (10) R. Docampo & S.N. Moreno; Drug Metab. Rev. 22, 161 (1990) (Review) | (11) W.J. Bodziak; Forensic Sci. Int. 82, 45 (1996) | (12) Y. Yang, et al.; Electrophoresis 22, 855 (2001) | (13) R. Coico, et al.; Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. Appendix 3-3C (2005) | (14) V.S. Sukumaran & A. Ramalingam; Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 63, 673 (2006) | (15) A.M. Maley, et al.; Exp. Dermatol. 22, 775 (2013) (Review) | (16) M. Feoktistova, et al.; Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, pdb.prot087379 (2016)