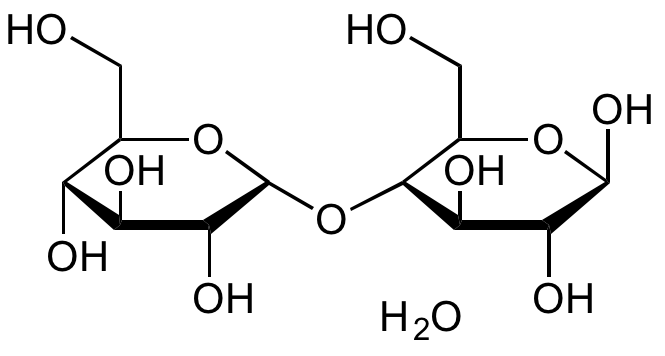
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-M0226-G100 | 100 g | £48.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-M0226-G500 | 500 g | £126.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
4-O-alpha-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose; Maltobiose
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
6363-53-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C12H22O11.H2O/c13-1-3-5(15)6(16)9(19)12(22-3)23-10-4(2-14)21-11(20)8(18)7(10)17;/h3-20H,1-2H2;1H2/t3-,4-,5-,6+,7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-;/m1./s1
InChiKey:
WSVLPVUVIUVCRA-QIJXJVNFSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 6363-53-7. Formula: C12H22O11 . H2O. MW: 342.29 . 18.02. D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is a component of starch and glycogen. It is a sugar composed of 2 alpha-D-glucose molecules coupled by an alpha(1?4) glycosidic bond. It is a reducing sugar with one anomeric carbon not linked in an anomeric bond. It contains a hemiacetal function and can mutarotate. Maltose is one product generated from starch and glycogen by the action of alpha-amylase. Maltose can be further hydrolyzed to glucose by the action of alpha-glucosidase (maltase), an enzyme commonly found in yeast and many other sources. It is called malt sugar when it is formed in fermenting grains during the production of alcoholic beverages. D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is used as a sweetener with about one-third the sweetness of sucrose and as a nutrient in culture media. It is used in pharmaceutical formulations and as a parenteral supplement of sugar for diabetics. In addition it can be used in cell culture studies or may be employed as standard for the alpha-amylase and invertase assays.
MDL:
MFCD00149343
Molecular Formula:
C12H22O11 . H2O
Molecular Weight:
342.29 . 18.02
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is a component of starch and glycogen. It is a sugar composed of 2 alpha-D-glucose molecules coupled by an alpha(1?4) glycosidic bond. It is a reducing sugar with one anomeric carbon not linked in an anomeric bond. It contains a hemiacetal function and can mutarotate. Maltose is one product generated from starch and glycogen by the action of alpha-amylase. Maltose can be further hydrolyzed to glucose by the action of alpha-glucosidase (maltase), an enzyme commonly found in yeast and many other sources. It is called malt sugar when it is formed in fermenting grains during the production of alcoholic beverages. D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is used as a sweetener with about one-third the sweetness of sucrose and as a nutrient in culture media. It is used in pharmaceutical formulations and as a parenteral supplement of sugar for diabetics. In addition it can be used in cell culture studies or may be employed as standard for the alpha-amylase and invertase assays.
Purity:
>90% (NMR)
SMILES:
OC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O1.O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (50mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) R. D'Ari; Res. Microbiol. 153, 425 (2002) (Review) | (2) Y. Lu & T.D. Sharkey; Plant Cell Environ. 29, 353 (2006) (Review)