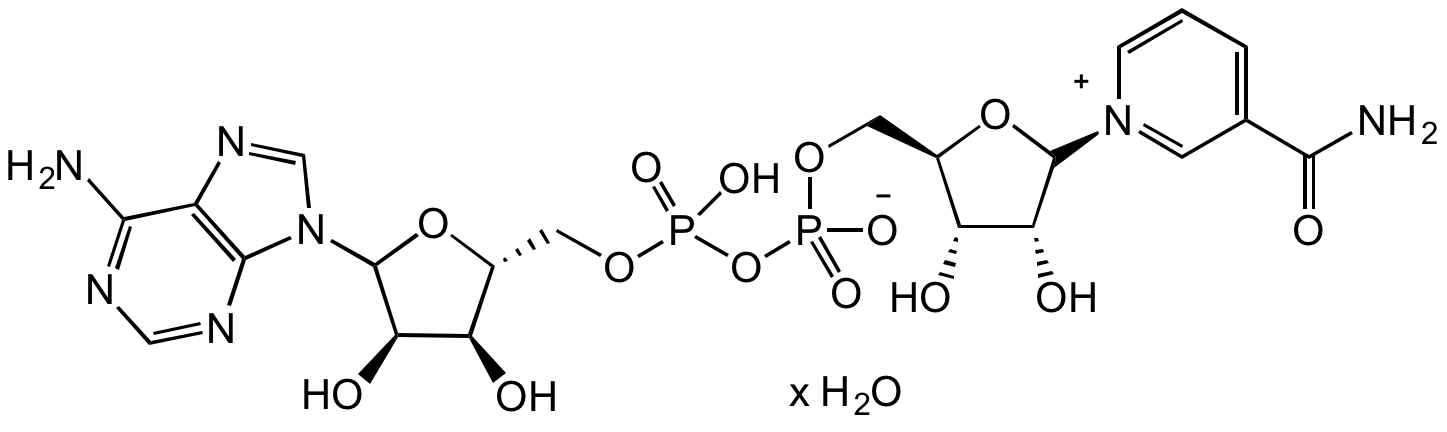
beta-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-N0222-G001 | 1 g | £59.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-N0222-G005 | 5 g | £157.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-N0222-G010 | 10 g | £255.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
beta-DPN; beta-NAD; Coenzyme 1; Cozymase; DPN; Diphosphopyridine nucleotide; NAD; Nadide; NSC 20272
Appearance:
White to yellow powder.
CAS:
53-84-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C21H27N7O14P2/c22-17-12-19(25-7-24-17)28(8-26-12)21-16(32)14(30)11(41-21)6-39-44(36,37)42-43(34,35)38-5-10-13(29)15(31)20(40-10)27-3-1-2-9(4-27)18(23)33/h1-4,7-8,10-11,13-16,20-21,29-32H,5-6H2,(H5-,22,23,24,25,33,34,35,36,37)/t10-,11-,13-,14-,15-,16-,20+,21?/m1/s1
InChiKey:
BAWFJGJZGIEFAR-OMYDKTABSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 53-84-9. Formula: C21H27N7O14P2 . xH2O. MW: 663.43 (anhydrous basis). NAD+, known more formally as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a signaling molecule as well as a cofactor or substrate for many enzymes. It acts as an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules while being converted to its reduced form, NADH. NAD+ is also essential for the activity of several enzymes, including poly(ADP)-ribose polymerases and cADP-ribose synthases. For example, it is used by some sirtuins to mediate protein deacetylation, producing O-acetyl-ADP-ribose and nicotinamide as well as the deacetylated protein. NAD+ is an important player and factor to research metabolic pathways and pathologies.
MDL:
MFCD00036253
Molecular Formula:
C21H27N7O14P2 . xH2O
Molecular Weight:
663.43 (anhydrous basis)
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
NAD+, known more formally as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a signaling molecule as well as a cofactor or substrate for many enzymes. It acts as an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules while being converted to its reduced form, NADH. NAD+ is also essential for the activity of several enzymes, including poly(ADP)-ribose polymerases and cADP-ribose synthases. For example, it is used by some sirtuins to mediate protein deacetylation, producing O-acetyl-ADP-ribose and nicotinamide as well as the deacetylated protein. NAD+ is an important player and factor to research metabolic pathways and pathologies.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
O[C@H]1C(N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N)O[C@H](COP(O)(OP(OC[C@@H]4[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]([N+]5=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C5)O4)([O-])=O)=O)[C@H]1O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) B. Schwer & E. Verdin; Cell Metabolism 7, 104 (2008) (Review) | (2) R.H. Houtkooper, et al.; Endocr. Rev. 31, 194 (2010) (Review) | (3) Y.S. Elhassan, et al.; J. Endocr. Soc. 1, 816 (2017) (Review)