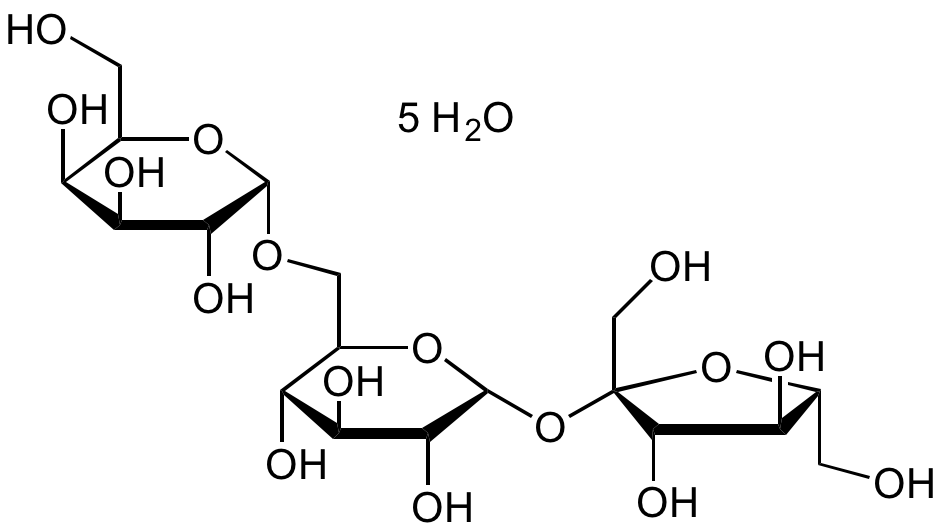
D-(+)-Raffinose pentahydrate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-R0082-G025 | 25 g | £53.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-R0082-G100 | 100 g | £139.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Antibody Isotype: n/a
Antibody Clone: n/a
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
O-alpha-D-Galactopyranosyl-(1->6)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl; beta-D-fructofuranoside; Melitose; Melitriose
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
17629-30-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C18H32O16/c19-1-5-8(22)11(25)13(27)16(31-5)30-3-7-9(23)12(26)14(28)17(32-7)34-18(4-21)15(29)10(24)6(2-20)33-18/h5-17,19-29H,1-4H2/t5-,6-,7-,8+,9-,10-,11+,12+,13-,14-,15+,16+,17-,18+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
MUPFEKGTMRGPLJ-ZQSKZDJDSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 17629-30-0. Formula: C18H32O16 . 5H2O. MW: 594.51. D-(+)-Raffinose is a trisaccharide composed of galactose, glucose, and fructose that occurs naturally in a variety of vegetables and grains. It is hydrolyzed to galactose and sucrose by alpha-galactosidase. Shown to have impacts on the immune system.
MDL:
MFCD00071590
Molecular Formula:
C18H32O16 . 5H2O
Molecular Weight:
594.51
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
D-(+)-Raffinose is a trisaccharide composed of galactose, glucose, and fructose that occurs naturally in a variety of vegetables and grains. It is hydrolyzed to galactose and sucrose by alpha-galactosidase. Shown to have impacts on the immune system.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
OC[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](OC[C@@H]2[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@]3(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O3)O2)O1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble DMSO, DMF or water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from plant source.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) T. Nagura, et al.; Br. J. Nutr. 88, 421 (2002) | (2) M. Knaupp, et al.; Planta 234, 477 (2011) | (3) W. Van den Ende; Front. Plant Sci. 4 247 (2013) | (4) H.S. Kim, et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 25318 (2016)