Parkin (E3 Ligase) (human) (rec.) (His)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| SBB-CE0055-C050 | 50 ug | £525.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Shipping:
Dry Ice
Storage:
-80°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
PARK2; E3 Ubiquitin-protein Ligase Parkin; Parkin RBR E3 Ubiquitin-protein Ligase; Parkinson Juvenile Disease Protein 2; Parkinson Disease Protein 2; PRKN
Concentration:
Lot dependent.
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Liquid. In 50mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 200mM sodium chloride, 10% glycerol, 5mM TCEP.
Handling Advice:
Aliquot to avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Long Description:
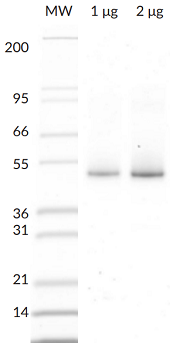
Protein. Human Parkin (Accession Nr. O60260) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag. Source: Sf9 cells. Liquid. In 50mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 200mM sodium chloride, 10% glycerol, 5mM TCEP. Purity: >95% (SDS-PAGE). Parkin (Parkinson juvenile disease protein 2) is a ~52kDa E3 Ligase enzyme protein, encoded by the PARK2 gene. It plays an important role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system and acts as a regulator of protein breakdown. Parkin is located in the cytoplasma until a sustained depolarization occurs after which it is translocated to the mitochondrial membrane and induces the degradation of various membrane proteins. Parkin mutation leads to the accumulation of missfolded, aggregated proteins and degenerated mitochondria. The role of these changes in the pathomechanism of neurodegenerative diseases is well-known. Parkin mutation is responsible for about 50% of familial cases and for 10 to 20% of youth cases. Present views are that the improper regulation of protein aggregation and a dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system may be the common pathway of sporadic and hereditary Parkinson?s disease. In vitro, Parkin can be activated by treatment with recombinant PINK1, or addition of low concentrations of pS65-phosphoubiquitin. Parkin has been reported to generate poly-Ubiquitin chains in K6, K11, K48, and K63 linkages both in vitro and in vivo.
Molecular Weight:
~52kDa
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Parkin (Parkinson juvenile disease protein 2) is a ~52kDa E3 Ligase enzyme protein, encoded by the PARK2 gene. It plays an important role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system and acts as a regulator of protein breakdown. Parkin is located in the cytoplasma until a sustained depolarization occurs after which it is translocated to the mitochondrial membrane and induces the degradation of various membrane proteins. Parkin mutation leads to the accumulation of missfolded, aggregated proteins and degenerated mitochondria. The role of these changes in the pathomechanism of neurodegenerative diseases is well-known. Parkin mutation is responsible for about 50% of familial cases and for 10 to 20% of youth cases. Present views are that the improper regulation of protein aggregation and a dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system may be the common pathway of sporadic and hereditary Parkinson?s disease. In vitro, Parkin can be activated by treatment with recombinant PINK1, or addition of low concentrations of pS65-phosphoubiquitin. Parkin has been reported to generate poly-Ubiquitin chains in K6, K11, K48, and K63 linkages both in vitro and in vivo.
Purity:
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Sequence:
Human Parkin (Accession Nr. O60260 https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O60260 ) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag.
Source / Host:
Sf9 cells
TAGs:
His
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Other Proteins
UNSPSC Number:
12352202
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -80°C.