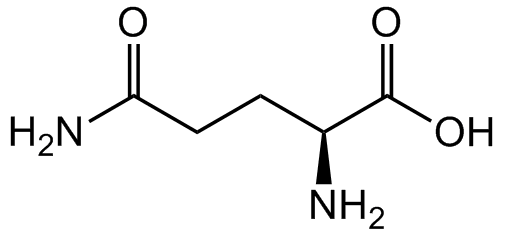
L-Glutamine [H-Gln-OH]
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3534-G001 | 1 g | £25.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3534-G005 | 5 g | £42.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
(+)-Glutamine; Levoglutamide; (S)-2,5-Diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid; L-Glutamic acid 5-amide; NSC 27421
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
56-85-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C5H10N2O3/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8/h3H,1-2,6H2,(H2,7,8)(H,9,10)/t3-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 56-85-9. Formula: C5H10N2O3. MW: 146.1. L-Glutamine is an amino acid and is essential in the formation of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, amino sugars, glutathione, L-glutamate and other amino acids as well as in protein synthesis and glucose production. It plays also a role in lipid synthesis (e.g. in cancer cells), cellular energy as a source next to glucose, nitrogen donation for many anabolic processes, including the synthesis of purines and carbon donation, as a source refilling the citric acid cycle. It is a nontoxic transporter of ammonia in the blood circulation and a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate and GABA. L-Glutamine is an essential amino acid which is a crucial component of culture media that serves as a major energy source for cells in culture. L-Glutamine exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, next to its roles in cell proliferation and cancer. Levels of L-glutamine in human white adipose tissue (WAT) are linked with obesity-associated inflammation. Addition of L-glutamine in obese mice attenuated adipose tissue inflammation. Reduced L-glutamine levels during obesity shift the balance from glutaminolysis toward glycolysis, leading to nuclear O-GlcNAcylation, which activates inflammation.
MDL:
MFCD00008044
Molecular Formula:
C5H10N2O3
Molecular Weight:
146.1
Other data:
Note: L-Glutamine is very stable as a dry powder and as a frozen solution. In liquid media or stock solutions, however, L-glutamine degrades relatively rapidly. The rate at which degradation proceeds is a function of time, temperature and pH. If used as a cell culture supplement, a 200mM stock solution (29.2mg/ml L-glutamine in 0.85% NaCl) can be prepared. The optimal concentration is dependent upon the cell type and medium used to culture the cells, but generally falls in the range of 2-6mM.
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
L-Glutamine is an amino acid and is essential in the formation of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, amino sugars, glutathione, L-glutamate and other amino acids as well as in protein synthesis and glucose production. It plays also a role in lipid synthesis (e.g. in cancer cells), cellular energy as a source next to glucose, nitrogen donation for many anabolic processes, including the synthesis of purines and carbon donation, as a source refilling the citric acid cycle. It is a nontoxic transporter of ammonia in the blood circulation and a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate and GABA. L-Glutamine is an essential amino acid which is a crucial component of culture media that serves as a major energy source for cells in culture. L-Glutamine exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, next to its roles in cell proliferation and cancer. Levels of L-glutamine in human white adipose tissue (WAT) are linked with obesity-associated inflammation. Addition of L-glutamine in obese mice attenuated adipose tissue inflammation. Reduced L-glutamine levels during obesity shift the balance from glutaminolysis toward glycolysis, leading to nuclear O-GlcNAcylation, which activates inflammation.
Purity:
>99% (TLC)
SMILES:
NC(CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (30 mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
Therapeutic considerations of L-glutamine: a review of the literature: A.L. Miller; Altern. Med. Rev. 4, 239 (1999) (Review) | Why is L-glutamine metabolism important to cells of the immune system in health, postinjury, surgery or infection? P. Newsholme; J. Nutr. 131, 2515S (2001) (Review) | Role of L-glutamine in critical illness: new insights: D. Kelly & P.E. Wischmeyer; Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 6, 217 (2003) (Review) | Glutamate synthase: a fascinating pathway from L-glutamine to L-glutamate: R.H. van den Heuvel, et al.; Cell Mol. Life Sci. 61, 669 (2004) (Review) | Supplementation with L-glutamine prevents tumor growth and cancer-induced cachexia as well as restores cell proliferation of intestinal mucosa of Walker-256 tumor-bearing rats: H.A. Martins, et al.; Amino Acids 48, 2773 (2016) | Glutamine Links Obesity to Inflammation in Human White Adipose Tissue: P. Petrus, et al.; Cell Metab. 31, 375 (2020)