AST-487
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3745-M001 | 1 mg | £35.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3745-M005 | 5 mg | £100.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3745-M025 | 25 mg | £370.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
AST487; NVP-AST-487
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
630124-46-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
InChi:
InChI=1S/C26H30F3N7O2/c1-3-35-10-12-36(13-11-35)16-18-4-5-20(14-22(18)26(27,28)29)34-25(37)33-19-6-8-21(9-7-19)38-24-15-23(30-2)31-17-32-24/h4-9,14-15,17H,3,10-13,16H2,1-2H3,(H,30,31,32)(H2,33,34,37)
InChiKey:
ODPGGGTTYSGTGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 630124-46-8. Formula: C26H30F3N7O2. MW: 529.6. AST487 is an inhibitor of RET (IC50 = 0.88µM), FLT3 (Ki = 0.52µM), KDR (IC50 = 0.17µM), c-Abl (IC50 = 0.02µM) and c-Kit (IC50 = 0.5µM).
AST-487 has been shown to inhibit RET autophosphorylation and activation of downstream effectors and to prevent the growth of human thyroid cancer cell lines with activating mutations of RET but not of lines without RET mutations. In xenografts of NIH3T3 cells expressing oncogenic RET and of the MTC cell line TT in nude mice, AST-487 dose dependently inhibited tumor growth.
AST-487, which selectively targets mutant FLT3 protein kinase activity, is also shown to override PKC412 resistance in vitro, and has significant antileukemic activity in an in vivo model of FLT3-ITD(+) leukemia. The combination of AST-487 with standard chemotherapeutic agents leads to enhanced inhibition of proliferation of mutant FLT3-expressing cells. AST-487 displays high selectivity and potency toward FLT3 as a molecular target, and could potentially be used to override drug resistance in AML.
MDL:
MFCD11983171
Molecular Formula:
C26H30F3N7O2
Molecular Weight:
529.6
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
AST487 is an inhibitor of RET (IC50 = 0.88µM), FLT3 (Ki = 0.52µM), KDR (IC50 = 0.17µM), c-Abl (IC50 = 0.02µM) and c-Kit (IC50 = 0.5µM). AST-487 has been shown to inhibit RET autophosphorylation and activation of downstream effectors and to prevent the growth of human thyroid cancer cell lines with activating mutations of RET but not of lines without RET mutations. In xenografts of NIH3T3 cells expressing oncogenic RET and of the MTC cell line TT in nude mice, AST-487 dose dependently inhibited tumor growth. AST-487, which selectively targets mutant FLT3 protein kinase activity, is also shown to override PKC412 resistance in vitro, and has significant antileukemic activity in an in vivo model of FLT3-ITD(+) leukemia. The combination of AST-487 with standard chemotherapeutic agents leads to enhanced inhibition of proliferation of mutant FLT3-expressing cells. AST-487 displays high selectivity and potency toward FLT3 as a molecular target, and could potentially be used to override drug resistance in AML.
Purity:
>95%
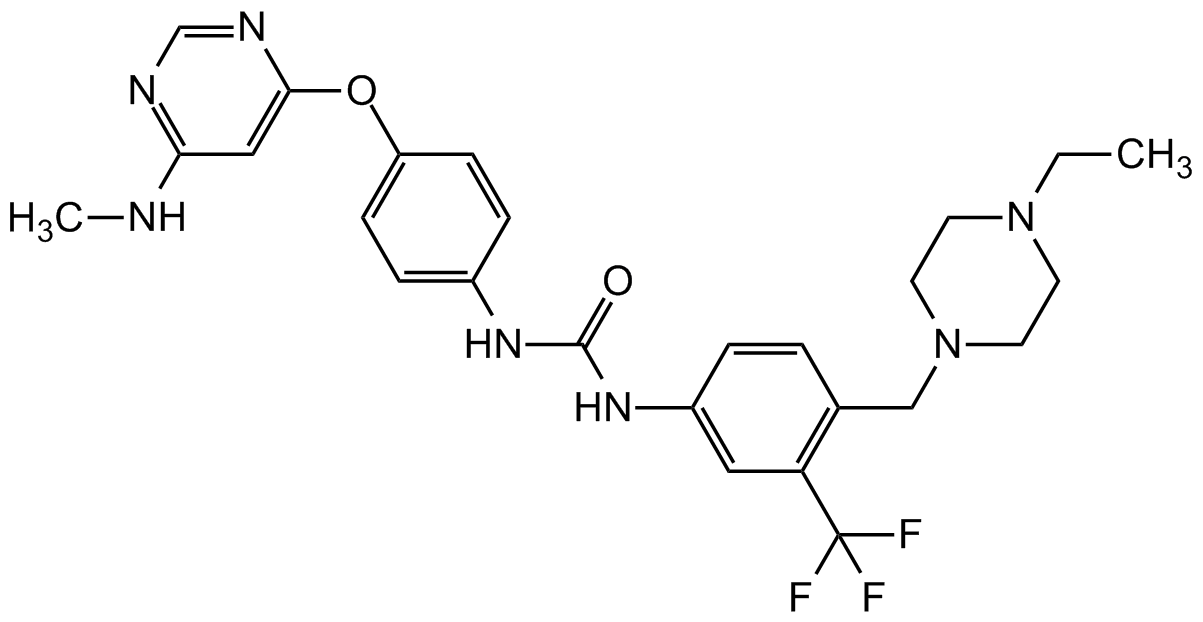
SMILES:
CCN1CCN(CC2=C(C=C(NC(=O)NC3=CC=C(OC4=CC(NC)=NC=N4)C=C3)C=C2)C(F)(F)F)CC1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, DMF or ethanol.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Protein Kinase Modulators
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
The RET kinase inhibitor NVP-AST487 blocks growth and calcitonin gene expression through distinct mechanisms in medullary thyroid cancer cells: N. Akeno-Stuart, et al.; Cancer Res. 67, 6956 (2007) | Antileukemic effects of the novel, mutant FLT3 inhibitor NVP-AST487: effects on PKC412-sensitive and -resistant FLT3-expressing cells: E. Weisberg, et al.; Blood 112, 5161 (2008) | Antileukemic Effects of Novel First- and Second-Generation FLT3 Inhibitors: Structure-Affinity Comparison: E. Weisberg, et al.; Genes Cancer. 1, 1021 (2010) | Targeting mTOR in RET mutant medullary and differentiated thyroid cancer cells: M.L. Gild, et al.; Endocr. Relat. Cancer 20, 659 (2013) | Targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase RET in combination with aromatase inhibitors in ER positive breast cancer xenografts: E. Andreucci, et al.; Oncotarget 7, 80543 (2016)