anti-AR (ARv7 Splice Variant) (human) Rabbit Monoclonal (RM7)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| REV-31-1109-00-R100 | 100 ul | £688.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Antibody Isotype: Rabbit IgG
Antibody Clonality: Recombinant Antibody
Antibody Clone: RM7
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
Blue Ice
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Androgen Receptor; Dihydrotestosterone Receptor; Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 3 Group C Member 4
Concentration:
N/A
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Handling Advice:
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Immunogen:
A peptide corresponding to AR splice variant 7.
Long Description:
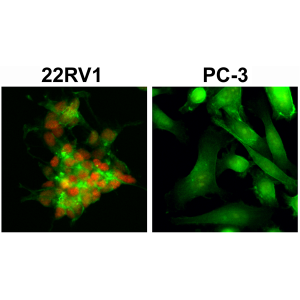
Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7). No cross reactivity with wild type androgen receptor. Applications: WB, ICC, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The androgen receptor (AR) is a member of the steroid-hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear receptors. The receptor is more than 90 kDa and has three major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and the androgen-binding domain. The androgen receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor that binds active testosterone (T) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. The AR signaling pathway plays a key role in development and function of male reproductive organs, including the prostate and epididymis. AR also plays a role in nonreproductive organs, such as muscle, hair follicles, and brain. Androgen Receptor is a phosphoprotein, and also regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). The inhibition of the MEK1/2 pathway correlates directly with a change in phosphorylation state of the androgen receptor. Abnormalities in the AR signaling pathway have been linked to a number of diseases, including prostate cancer, Kennedy's disease, and male infertility. Mutations in this gene are associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). The AR3 or ARv7 isoform, which lacks the typical ligand binding domain, is created through the alternative splicing of cryptic exons. ARv7 is frequently expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and while dependent on the activity of the full-length androgen receptor (AR-FL), ARv7 can activate a completely distinct transcriptional program.
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
P10275
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
The androgen receptor (AR) is a member of the steroid-hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear receptors. The receptor is more than 90 kDa and has three major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and the androgen-binding domain. The androgen receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor that binds active testosterone (T) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. The AR signaling pathway plays a key role in development and function of male reproductive organs, including the prostate and epididymis. AR also plays a role in nonreproductive organs, such as muscle, hair follicles, and brain. Androgen Receptor is a phosphoprotein, and also regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). The inhibition of the MEK1/2 pathway correlates directly with a change in phosphorylation state of the androgen receptor. Abnormalities in the AR signaling pathway have been linked to a number of diseases, including prostate cancer, Kennedy's disease, and male infertility. Mutations in this gene are associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). The AR3 or ARv7 isoform, which lacks the typical ligand binding domain, is created through the alternative splicing of cryptic exons. ARv7 is frequently expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and while dependent on the activity of the full-length androgen receptor (AR-FL), ARv7 can activate a completely distinct transcriptional program.
Purity:
Protein A purified.
Source / Host:
Rabbit
Specificity:
This antibody reacts to androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7). No cross reactivity with wild type androgen receptor.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Primary Antibodies
UNSPSC Number:
12352203
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.