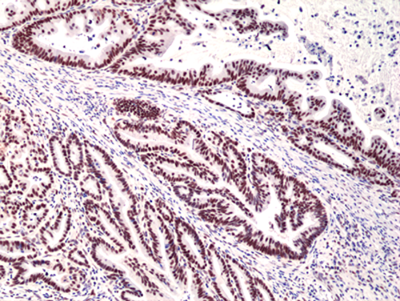
anti-MSH3 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal (RM405)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| REV-31-1291-00-R100 | 100 ul | £455.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Antibody Isotype: Rabbit IgG
Antibody Clonality: Recombinant Antibody
Antibody Clone: RM405
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
Blue Ice
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
DNA Mismatch Repair Protein Msh3; Divergent Upstream Protein; DUP; MRP1;
Concentration:
N/A
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Handling Advice:
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Immunogen:
A peptide corresponding to residues near the N-terminus of human MSH3.
Long Description:
Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human to MSH3. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The mismatch repair (MMR) proteins are required to maintain genomic integrity in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, by correcting single mismatches and short unpaired regions, such as small insertions and deletions. In eukaryotes, three proteins are involved in mismatch recognition, MSH2, MSH3 and MSH6. The three proteins form two heterodimers MutSalpha (MSH2-MSH6) and MutSbeta (MSH2-MSH3). MutSalpha is thought to be involved primarily in the recognition and repair of base-base mismatches and small insertion/deletion loops. MutSbeta acts preferentially on insertion/deletion loops up to 12 nucleotides in length. The MSH2, MSH3, and PMS2 mismatch repair proteins are also involved in other DNA repair pathways such as single-strand annealing and homologous recombination, anti-recombination, DNA damage signaling, apoptosis, as well as site-specific mutagenesis during immunoglobin somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. They interact with several other oncogenic targets, including ATR, BRCA1 or p53. Deficiencies in expression of DNA repair genes underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, DNA damage tends to accumulate. Such excess DNA damage may increase mutations due to error-prone translesion synthesis and error prone repair. Elevated DNA damage may also increase epigenetic alterations due to errors during DNA repair. Such mutations and epigenetic alterations may give rise to cancer. Loss of MSH3 can lead to mismatch repair deficiency and genetic instability which have been identified as particularly common carcinogenic effects in human colorectal cancer. Mutations causing MSH3 knockdown can lead to diminished capacity for cells to repair long insertion/deletion loops causing microsatellite instabilities (MSI) in the genome and allowing an increase in the rates of somatic mutation.
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
P20585
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
The mismatch repair (MMR) proteins are required to maintain genomic integrity in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, by correcting single mismatches and short unpaired regions, such as small insertions and deletions. In eukaryotes, three proteins are involved in mismatch recognition, MSH2, MSH3 and MSH6. The three proteins form two heterodimers MutSalpha (MSH2-MSH6) and MutSbeta (MSH2-MSH3). MutSalpha is thought to be involved primarily in the recognition and repair of base-base mismatches and small insertion/deletion loops. MutSbeta acts preferentially on insertion/deletion loops up to 12 nucleotides in length. The MSH2, MSH3, and PMS2 mismatch repair proteins are also involved in other DNA repair pathways such as single-strand annealing and homologous recombination, anti-recombination, DNA damage signaling, apoptosis, as well as site-specific mutagenesis during immunoglobin somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. They interact with several other oncogenic targets, including ATR, BRCA1 or p53. Deficiencies in expression of DNA repair genes underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, DNA damage tends to accumulate. Such excess DNA damage may increase mutations due to error-prone translesion synthesis and error prone repair. Elevated DNA damage may also increase epigenetic alterations due to errors during DNA repair. Such mutations and epigenetic alterations may give rise to cancer. Loss of MSH3 can lead to mismatch repair deficiency and genetic instability which have been identified as particularly common carcinogenic effects in human colorectal cancer. Mutations causing MSH3 knockdown can lead to diminished capacity for cells to repair long insertion/deletion loops causing microsatellite instabilities (MSI) in the genome and allowing an increase in the rates of somatic mutation.
Purity:
Protein A purified.
Source / Host:
Rabbit
Specificity:
This antibody reacts to human to MSH3.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Primary Antibodies
UNSPSC Number:
12352203
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.