CA77.1 [CMA Activator]
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-0165-M005 | 5 mg | £75.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-0165-M025 | 25 mg | £270.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +4°C, Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
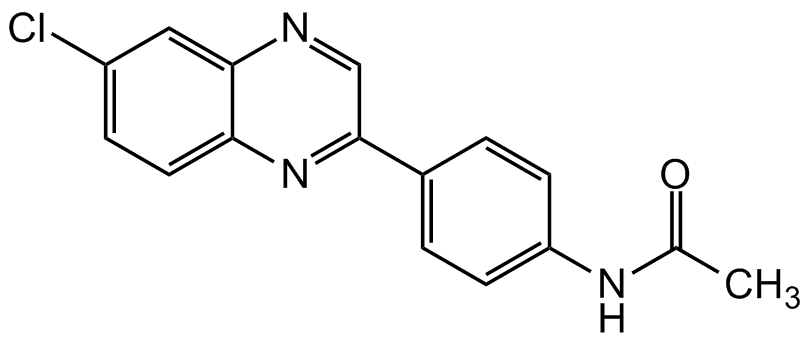
N-[4-(6-Chloroquinoxalin-2-yl)phenyl]acetamide
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
2412270-22-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C16H12ClN3O/c1-10(21)19-13-5-2-11(3-6-13)16-9-18-15-8-12(17)4-7-14(15)20-16/h2-9H,1H3,(H,19,21)
InChiKey:
ZQXMPDVGBWOTBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 2412270-22-3. Formula: C16H12ClN3O. MW: 297.7. CA77.1 is a novel selective chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) activator by increasing the expression of the lysosomal receptor for this pathway, LAMP2A, in lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), is a selective autophagy shown to degrade neurodegeneration-related proteins such as alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) or tau. Loss of neuronal CMA leads to altered neuronal function, selective changes in the neuronal metastable proteome and proteotoxicity. Chemical upregulation of CMA has been shown to ameliorate pathology in AD experimental mouse models, reduce brain pathology and improve disease phenotype.
CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vitro and in vivo (in contrary to it's derivative AR7 which was not suitable for in vivo application). CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vivo, and demonstrates brain penetrance and favorable pharmacokinetics. It has been shown in animal studies that administration of CA77.1 to enhance chaperone-mediated autophagy, may help to degrade toxic pathogenic protein products such as tau proteins and has potential applications in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
MDL:
MFCD00045388
Molecular Formula:
C16H12ClN3O
Molecular Weight:
297.7
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
CA77.1 is a novel selective chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) activator by increasing the expression of the lysosomal receptor for this pathway, LAMP2A, in lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), is a selective autophagy shown to degrade neurodegeneration-related proteins such as alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) or tau. Loss of neuronal CMA leads to altered neuronal function, selective changes in the neuronal metastable proteome and proteotoxicity. Chemical upregulation of CMA has been shown to ameliorate pathology in AD experimental mouse models, reduce brain pathology and improve disease phenotype. CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vitro and in vivo (in contrary to it's derivative AR7 which was not suitable for in vivo application). CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vivo, and demonstrates brain penetrance and favorable pharmacokinetics. It has been shown in animal studies that administration of CA77.1 to enhance chaperone-mediated autophagy, may help to degrade toxic pathogenic protein products such as tau proteins and has potential applications in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
ClC1=CC=C(N=C(C2=CC=C(NC(C)=O)C=C2)C=N3)C3=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml). Almost insoluble in other tested solvents, like MeOH, EtOH or water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Chaperone-mediated autophagy prevents collapse of the neuronal metastable proteome: M. Bourdenx, et al.; Cell 184, (2021)