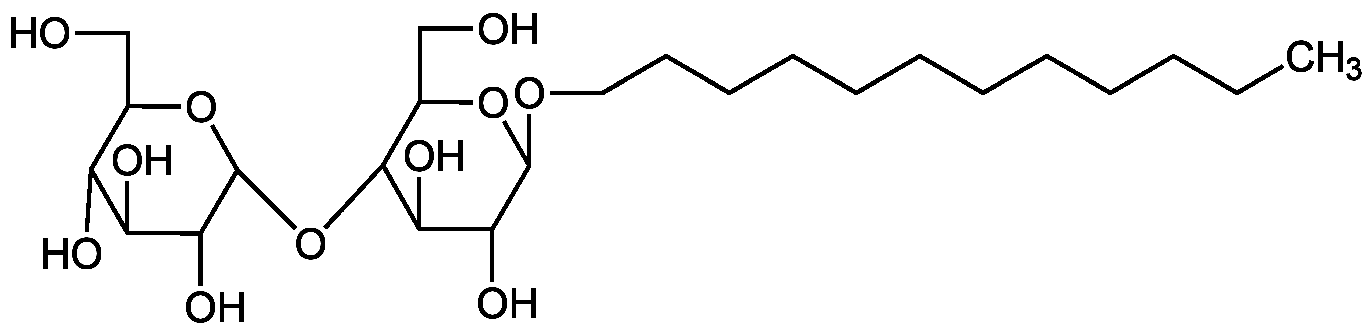
n-Dodecyl-beta-D-maltoside (high purity)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CC1-0010-G001 | 1 g | £60.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CC1-0010-G005 | 5 g | £160.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CC1-0010-G025 | 25 g | £600.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +4°C, Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
DDM; n-Dodecyl-beta-maltoside; Lauryl-beta-maltoside; Dodecyl-beta-D-maltopyranoside
Appearance:
White powder.
CAS:
69227-93-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Hygroscopic.Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C24H46O11/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-32-23-21(31)19(29)22(16(14-26)34-23)35-24-20(30)18(28)17(27)15(13-25)33-24/h15-31H,2-14H2,1H3/t15-,16-,17-,18+,19-,20-,21-,22-,23-,24-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
NLEBIOOXCVAHBD-QKMCSOCLSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 69227-93-6. Formula: C24H46O11. MW: 510.6. Water-soluble non-ionic detergent with a hydrophilic maltose head and a hydrophobic long chain alkyl tail. It is considered a gentle detergent that is more efficient than other detergents. For functional solubilization and purification of membrane proteins. It helps to retain the native conformation and activity of membrane-associated proteins and facilitates the reforming of these proteins after denaturation. For the stabilization and activation of enzymes. The critical micelle concentration of DDM is approx. 0.18 mM in water, decreases in the presence of sodium chloride or sucrose and increases in urea.
MDL:
MFCD00043012
Molecular Formula:
C24H46O11
Molecular Weight:
510.6
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Water-soluble non-ionic detergent with a hydrophilic maltose head and a hydrophobic long chain alkyl tail. It is considered a gentle detergent that is more efficient than other detergents. For functional solubilization and purification of membrane proteins. It helps to retain the native conformation and activity of membrane-associated proteins and facilitates the reforming of these proteins after denaturation. For the stabilization and activation of enzymes. The critical micelle concentration of DDM is approx. 0.18 mM in water, decreases in the presence of sodium chloride or sucrose and increases in urea.
Purity:
>99% (HPLC) | [alpha-Isomer <2.0% (HPLC)] | [n-Dodecanol <0.005% (HPLC)]
SMILES:
CCCCCCCCCCCCOC1OC(CO)C(OC2OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C1O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water or 100% ethanol.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 3 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Synthesis and properties of some alpha-D-alkyl glucosides and mannosides: apparent molal volumes and solubilization of nitrobenzene in water at 25°C: G.M. Brown, et al.; Can. J. Chem. 48, 2525 (1970) | Detergent-mediated reconstitution of membrane proteins: J. Knol, et al.; Biochem. 37, 16410 (1998) | The vesicle-to-micelle transition of phosphatidylcholine vesicles induced by nonionic detergents: Effects of sodium chloride, sucrose and urea: A. Walter, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1508, 20 (2000) | Macromolecular Crystallography Protocols: S. Doublie; Methods Mol. Biol. 363, (2007) | Detergents for the stabilization and crystallization of membrane proteins: G.G. Prive; Methods 41, 388 (2007) | The use of detergents to purify membrane proteins; T. Arnold & D. Linke; Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. Chapter 4: Unit 4.8.1-4.8.30 (2008) | Expression, purification and in vitro functional reconstitution of the chemokine receptor CCR1: S.J. Allen, et al.; Prot. Expr. Purif. 66, 73 (2009) | Structuring detergents for extracting and stabilizing functional membrane proteins: R. Matar-Merheb, et al.; PLoS One 6, e18036 (2011) | Efficiency of detergents at maintaining membrane protein structures in their biologically relevant forms: D.V. Tulumello & C.M. Deber; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1818, 1351 (2012) | High-throughput stability screening for detergent-solubilized membrane proteins: V. Kotov, et al.; Sci. Rep. 9, 10379 (2019)