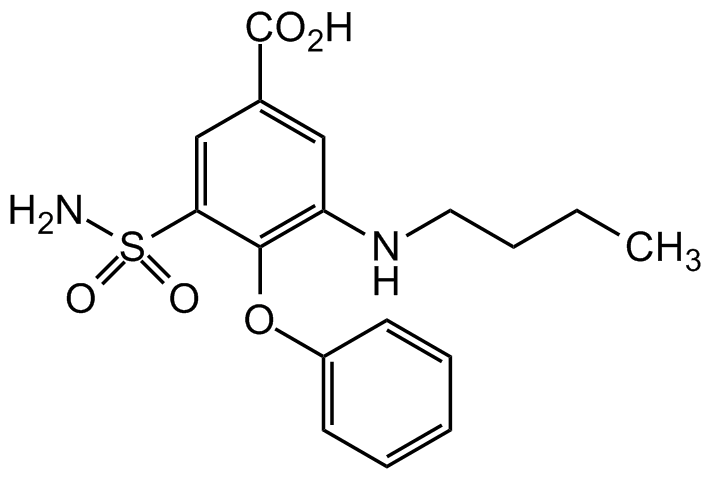
Bumetanide
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3543-M250 | 250 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3543-G001 | 1 g | £85.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3543-G005 | 5 g | £250.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +4°C, Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
PF-1593; Ro 10-6338; 3-(Aminosulfonyl)-5-(butylamino)-4-phenoxybenzoic acid
Appearance:
Off-white to white powder.
CAS:
28395-03-1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C17H20N2O5S/c1-2-3-9-19-14-10-12(17(20)21)11-15(25(18,22)23)16(14)24-13-7-5-4-6-8-13/h4-8,10-11,19H,2-3,9H2,1H3,(H,20,21)(H2,18,22,23)
InChiKey:
MAEIEVLCKWDQJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 28395-03-1. Formula: C17H20N2O5S. MW: 364.4. Bumetanide is a loop diuretic that is clinically used to treat congestive heart failure. Bumetanide also exhibits anxiolytic, neuroprotective and anti-epileptic/anticonvulsant activities. Bumetanide induces hyperpolarization in kidney cells, increasing whole-cell conductance and intracellular Ca2+ levels. Bumetanide acts by antagonizing Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter 1 (NKCC1), K+/Ca2+ co-transporter 2 (KCC2) and NKCC2, decreasing fluid secretion and Na+/K+ transport. While NKCC1 is expressed both in the CNS and in systemic organs, NKCC2 is kidney-specific. Bumetanide is a potent and specific inhibitor of Na-K-2Cl cotransporter 1 (NKCC1; IC50 = 0.68µM). It is selective for NKCC1 over NKCC2 (IC50 = 4µM). It is also an agonist of G protein-coupled receptor 35 (GPR35; EC50 = 10µM) and can inhibit carbonic anhydrases IX and XII. In physiological conditions, adult neurons have low intracellular Cl- levels underlying the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic inhibitory drive. Neurons have high (Cl-)I levels and excitatory GABA actions in a wide range of pathological conditions including spinal cord lesions, chronic pain, brain trauma, cerebrovascular infarcts, autism, Rett and Down syndrome, various types of epilepsies, and other genetic or environmental insults. By specifically inhibiting the chloride importer NKCC1, bumetanide efficiently restores low (Cl-)I levels and attenuates many disorders in experimental conditions. Bumetanide has been shown to improve electrophysiological, pathological and cognitive deficits in APOE4 knock-in mice. And single-nucleus RNA sequencing of neurons derived from APOE4 induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) showed transcriptomic reversal of Alzheimer?s disease (AD) signatures.
MDL:
MFCD00078949
Molecular Formula:
C17H20N2O5S
Molecular Weight:
364.4
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Bumetanide is a loop diuretic that is clinically used to treat congestive heart failure. Bumetanide also exhibits anxiolytic, neuroprotective and anti-epileptic/anticonvulsant activities. Bumetanide induces hyperpolarization in kidney cells, increasing whole-cell conductance and intracellular Ca2+ levels. Bumetanide acts by antagonizing Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter 1 (NKCC1), K+/Ca2+ co-transporter 2 (KCC2) and NKCC2, decreasing fluid secretion and Na+/K+ transport. While NKCC1 is expressed both in the CNS and in systemic organs, NKCC2 is kidney-specific. Bumetanide is a potent and specific inhibitor of Na-K-2Cl cotransporter 1 (NKCC1; IC50 = 0.68µM). It is selective for NKCC1 over NKCC2 (IC50 = 4µM). It is also an agonist of G protein-coupled receptor 35 (GPR35; EC50 = 10µM) and can inhibit carbonic anhydrases IX and XII. In physiological conditions, adult neurons have low intracellular Cl- levels underlying the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic inhibitory drive. Neurons have high (Cl-)I levels and excitatory GABA actions in a wide range of pathological conditions including spinal cord lesions, chronic pain, brain trauma, cerebrovascular infarcts, autism, Rett and Down syndrome, various types of epilepsies, and other genetic or environmental insults. By specifically inhibiting the chloride importer NKCC1, bumetanide efficiently restores low (Cl-)I levels and attenuates many disorders in experimental conditions. Bumetanide has been shown to improve electrophysiological, pathological and cognitive deficits in APOE4 knock-in mice. And single-nucleus RNA sequencing of neurons derived from APOE4 induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) showed transcriptomic reversal of Alzheimer?s disease (AD) signatures.
Purity:
>98%
SMILES:
NS(C1=CC(C(O)=O)=CC(NCCCC)=C1OC2=CC=CC=C2)(=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml), DMF (30mg/ml) or ethanol (15mg/ml). Insoluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues: S.M. O'Grady, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. 253, C177 (1987) | Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Interaction of indapamide and related diuretics with 12 mammalian isozymes and X-ray crystallographic studies for the indapamide-isozyme II adduct: C. Temperini, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 2567 (2008) | Diuretics: from classical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors to novel applications of the sulfonamides: C.T. Supuran; Curr. Pharm. Des. 14, 641 (2008) (Review) | The loop diuretic bumetanide blocks posttraumatic p75NTR upregulation and rescues injured neurons: A. Shulga, et al.; J. Neurosci. 32, 1757 (2012) | GPR35 is a target of the loop diuretic drugs bumetanide and furosemide: Y. Yang, et al.; Pharmacology 89, 13 (2012) | The search for NKCC1-selective drugs for the treatment of epilepsy: Structure-function relationship of bumetanide and various bumetanide derivatives in inhibiting the human cation-chloride cotransporter NKCC1A: K. Lykke, et al.; Epilepsy Behav. 59, 42 (2016) | NKCC1 Chloride Importer Antagonists Attenuate Many Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders: Y. Ben-Ari; Trends Neurosci. 40, 536 (2017) (Review) | Role of NKCC1 Activity in Glioma K+ Homeostasis and Cell Growth: New Insights With the Bumetanide-Derivative STS66: L. Luo, et al.; Front. Physiol.; 11, 911 (2020) | Role of NKCC1 and KCC2 in Epilepsy: From Expression to Function: R. Liu, et al.; Front. Neurol. 10, 1407 (2020) (Review) | Pharmacological tools to target NKCC1 in brain disorders: A. Savardi, et al.; Trends Pharmacol. Sci. (Epub ahead of print) (2021) (Review) | Experimental and real-world evidence supporting the computational repurposing of bumetanide for APOE4-related Alzheimer's disease: A. Taubes, et al.; Nature Aging 1, 932 (2021)