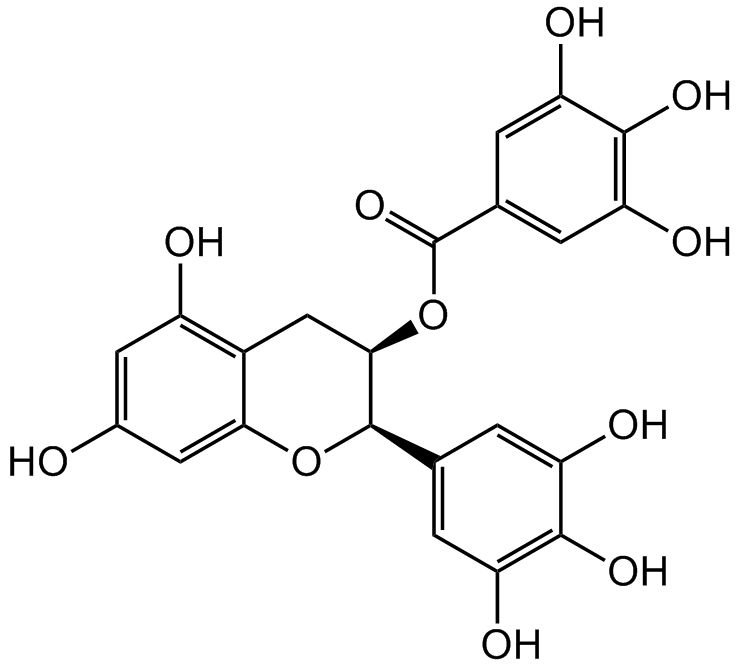
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-E0128-M010 | 10 mg | £126.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Plant
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +20°C Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
(-)-cis-3,3',4',5,5',7-Hexahydroxy-flavane-3-gallate; Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; EGCG; CCRIS 3729; Teavigo; NVP-XAA 723
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
989-51-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 989-51-5. Formula: C22H18O11. MW: 458.37. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory polyphenol flavonoid exerts antitumor properties by inhibiting telomerase and DNA methyltransferase activity. EGCG inhibits the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), MMP-9 and reduces the invasiveness. EGCG blocks the activation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2). Regulates cancer cell growth, proliferation, transformation, survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. EGCG increases bone mineral density and reduces bone resorption. EGCG inhibits osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) transcriptional activity. EGCG has neuroprotective and anti-aging property and increases myogenic differentiation. EGCG inhibits fatty acid synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase activity. EGCG has preventive cardiovascular and metabolic (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) effects and in vivo, EGCG reduces food intake and body weight, serum levels of insulin, leptin, testosterone and growth hormone.
MDL:
MFCD00075940
Molecular Formula:
C22H18O11
Molecular Weight:
458.37
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory polyphenol flavonoid exerts antitumor properties by inhibiting telomerase and DNA methyltransferase activity. EGCG inhibits the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), MMP-9 and reduces the invasiveness. EGCG blocks the activation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2). Regulates cancer cell growth, proliferation, transformation, survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. EGCG increases bone mineral density and reduces bone resorption. EGCG inhibits osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) transcriptional activity. EGCG has neuroprotective and anti-aging property and increases myogenic differentiation. EGCG inhibits fatty acid synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase activity. EGCG has preventive cardiovascular and metabolic (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) effects and in vivo, EGCG reduces food intake and body weight, serum levels of insulin, leptin, testosterone and growth hormone.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
OC1=CC([C@H]2OC3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C3C[C@H]2OC(C4=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C4)=O)=CC(O)=C1O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol (10 mg/ml), DMF (20 mg/ml), DMSO (20 mg/ml) or water (10 mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Plant
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) Y.J. Surh, et al.; Mutat. Res. 480-481, 243 (2001) (Review) | (2) J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 371, 199 (2003) | (3) N. Khan, et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 2500 (2006) (Review) | (4) W.X. Tian; Curr. Med. Chem. 13, 967 (2006) (Review) | (5) A. Murakami; Forum Nutr. 61, 193 (2009) (Review) | (6) H. Tachibana; Forum Nutr. 61, 156 (2009) (Review) | (7) S.C. Gupta, et al.; Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 405 (2010) (Review) | (8) H. Zhou, et al.; Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 10, 571 (2010) (Review) | (9) F.H. Sarkar, et al.; Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 383 (2010) (Review) | (10) S. Sae-tan, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 64, 146 (2011) (Review) | (11) M.K. Shanmugam, et al.; Nutr. Cancer 63, 161 (2011) (Review) | (12) G. Scapagnini, et al.; Mol. Neurobiol. 44, 192 (2011) (Review) | (13) C.B. Pocernich, et al.; Curr. Alzheimer Res. 8, 452 (2011) (Review) | (14) D. Wu, et al.; Mol. Aspects Med 33, 107 (2012) (Review)