Josamycin Solution (in acetone)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-J0009-L001 | 1 ml | £84.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-J0009-L005 | 5 ml | £230.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Kitasamycin A3; Leucomycin A3; Turimycin A5
Appearance:
Liquid.
CAS:
16846-24-5
Class:
3
Concentration:
10µg/ml in acetone
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS02,GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H225, H319, H336
InChi:
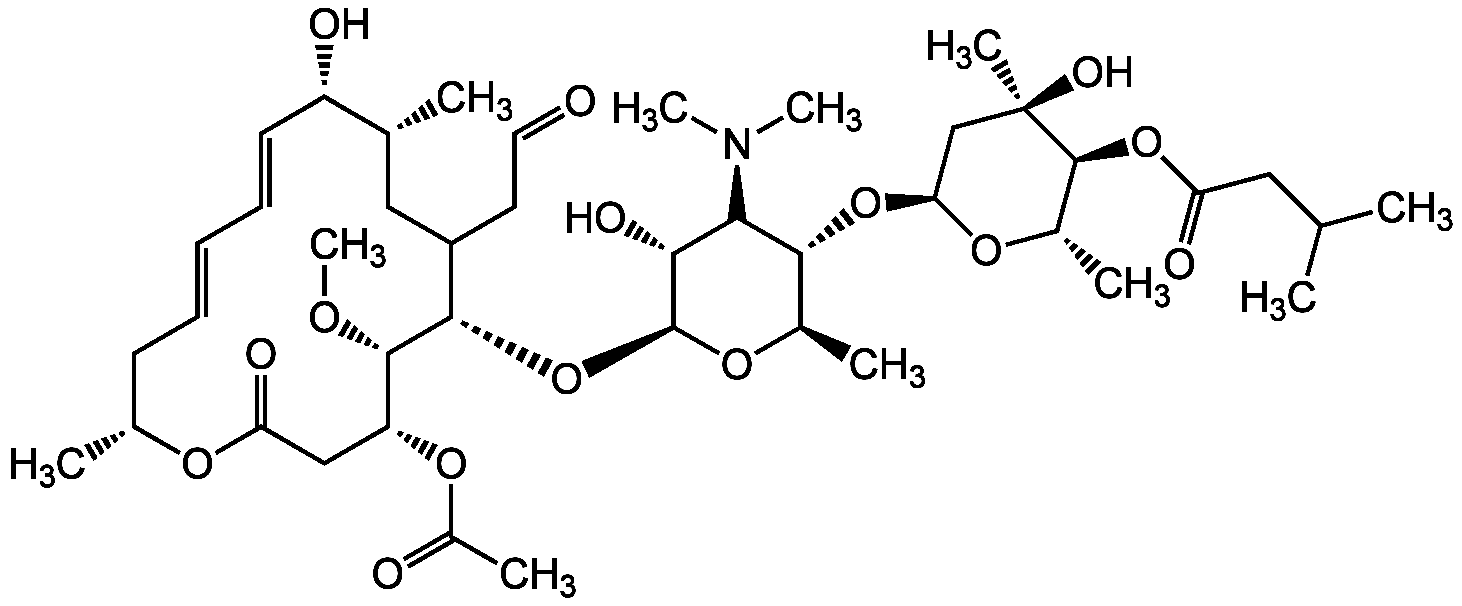
InChI=1S/C42H69NO15/c1-23(2)19-32(47)56-40-27(6)53-34(22-42(40,8)50)57-37-26(5)54-41(36(49)35(37)43(9)10)58-38-29(17-18-44)20-24(3)30(46)16-14-12-13-15-25(4)52-33(48)21-31(39(38)51-11)55-28(7)45/h12-14,16,18,23-27,29-31,34-41,46,49-50H,15,17,19-22H2,1-11H3/b13-12+,16-14+/t24-,25-,26-,27+,29?,30+,31-,34+,35+,36-,37-,38+,39+,40+,41+,42-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
XJSFLOJWULLJQS-LAEWXYAOSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 16846-24-5. Formula: C42H69NO15. MW: 827.99. Josamycin is a member of the leucomycin family of macrolide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces kitasatoensis. It is an antimicrobial against a wide variety of pathogens. It has activity against Gram-positive an Gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action is via inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis by binding reversibly to the subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting peptidyltransferase and ribosomal translocation, thereby inhibiting translocation of peptidyl tRNA. Josamycin may overcome anticancer drug resistance by inhibiting the binding of vinblastine or cyclosporin A to P-glycoprotein (Pgp). It is used to study the modification of phagocytosis and cytokine production by macrolide antibiotics and immunomodulatory effects.
MDL:
MFCD00211043
Molecular Formula:
C42H69NO15
Molecular Weight:
827.99
Package Type:
Vial
PG:
II
Precautions:
P210, P305 + P351 + P338, P370 + P378, P403 + P235
Product Description:
Josamycin is a member of the leucomycin family of macrolide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces kitasatoensis. It is an antimicrobial against a wide variety of pathogens. It has activity against Gram-positive an Gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action is via inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis by binding reversibly to the subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting peptidyltransferase and ribosomal translocation, thereby inhibiting translocation of peptidyl tRNA. Josamycin may overcome anticancer drug resistance by inhibiting the binding of vinblastine or cyclosporin A to P-glycoprotein (Pgp). It is used to study the modification of phagocytosis and cytokine production by macrolide antibiotics and immunomodulatory effects.
Purity:
>98% (UV)
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
O=C1O[C@H](C)C/C=C/C=C/[C@H](O)[C@H](C)CC(CC=O)[C@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@@H]3O[C@@H](C)[C@H](OC(CC(C)C)=O)[C@](C)(O)C3)[C@@H](N(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC(C)=O)C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Microbial
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
1090
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) K. Nitta, et al.; J. Antibiot. 20, 181 (1967) | (2) T. Osono, et al.; J. Antibiot. 20, 174 (1967) | (3) T. Bergan & B. Oydvin; Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. B Microbiol. Immunol. 80, 101 (1972) | (4) E.L. Westerman, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 9, 988 (1976) | (5) R.E. Reese, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 10, 253 (1976) | (6) J.P. Guggenbichler, et al.; Infection 21, 259 (1993) | (7) K. Morikawa, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 38, 2643 (1994) | (8) T. Ono, et al.; Chemotherapy 42, 159 (1996) | (9) L. Wang, et al.; Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 27, 587 (2000) | (10) M. Lovmar, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 53506 (2004) | (11) E.Y. Choi, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 105, 498 (2018)