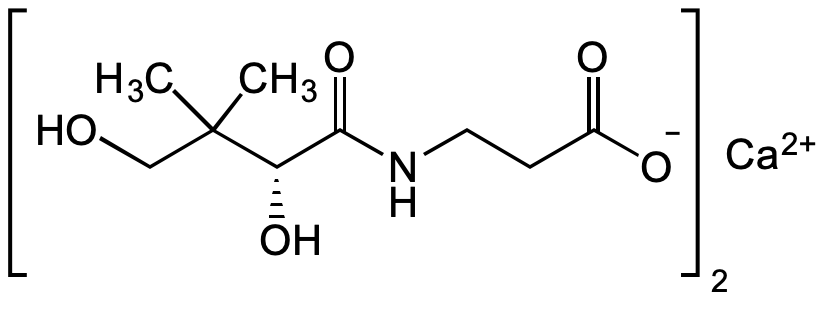
Calcium pantothenate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0657-G025 | 25 g | £72.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-C0657-G100 | 100 g | £205.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
(R)-(+)-N-(2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-beta-alanine hemicalcium salt; D-Pantothenic acid hemicalcium salt; Calcium D-pantothenate; Vitamin B5
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
137-08-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C9H17NO5.Ca/c1-9(2,5-11)7(14)8(15)10-4-3-6(12)13;/h7,11,14H,3-5H2,1-2H3,(H,10,15)(H,12,13);/q;+2/p-1/t7-;/m0./s1
InChiKey:
SXRRAEDIIGNDNU-FJXQXJEOSA-M
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 137-08-6. Formula: C9H16NO5 . 0.5Ca. MW: 238.27. Synthetic. Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) is a water-soluble vitamin, an essential nutrient required to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and fats. CoA is important in energy metabolism for pyruvate to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) as acetyl-CoA, and for alpha-ketoglutarate to be transformed to succinyl-CoA in the cycle. CoA is also important in the biosynthesis of many important compounds such as fatty acids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine. CoA is incidentally also required in the formation of ACP, which is also required for fatty acid synthesis in addition to CoA. Small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food, with high amounts in whole-grain cereals, legumes, eggs, meat, royal jelly, avocado and yogurt. Only the dextrorotatory (D) isomer possesses biological activity, such as antibacterial or metabolic properties.
MDL:
MFCD00002766
Molecular Formula:
C9H16NO5 . 0.5Ca
Molecular Weight:
238.27
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) is a water-soluble vitamin, an essential nutrient required to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and fats. CoA is important in energy metabolism for pyruvate to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) as acetyl-CoA, and for alpha-ketoglutarate to be transformed to succinyl-CoA in the cycle. CoA is also important in the biosynthesis of many important compounds such as fatty acids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine. CoA is incidentally also required in the formation of ACP, which is also required for fatty acid synthesis in addition to CoA. Small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food, with high amounts in whole-grain cereals, legumes, eggs, meat, royal jelly, avocado and yogurt. Only the dextrorotatory (D) isomer possesses biological activity, such as antibacterial or metabolic properties.
Purity:
>98%
SMILES:
OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(NCCC([O-])=O)=O.[Ca+2]
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (44mg/ml) or water (44mg/ml). Slightly soluble in ethanol (<1mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) P. Gardner, et al.; Food Chem. 68, 471 (2000) | (2) B. Ou, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 2772 (2002) | (3) T. Bahorun, et al.; J. Sci. Food Agric. 84, 1553 (2004) | (4) W. He, et al.; Front. Immunol. 9, 365 (2018) | (5) S. Patassini, et al.; Metabolites 9, E113 (2019) | (6) Q. Ma, et al.; Am. J. Transl. Res. 11, 5008 (2019)