Gram's fuchsin Solution
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-G0064-L250 | 250 ml | £35.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +20°C Long Term: +4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Fuchsin solution; Basic Red 9; Magenta O; Basic Violet 14
Appearance:
Dark red liquid.
CAS:
632-99-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS08
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H350
InChi:
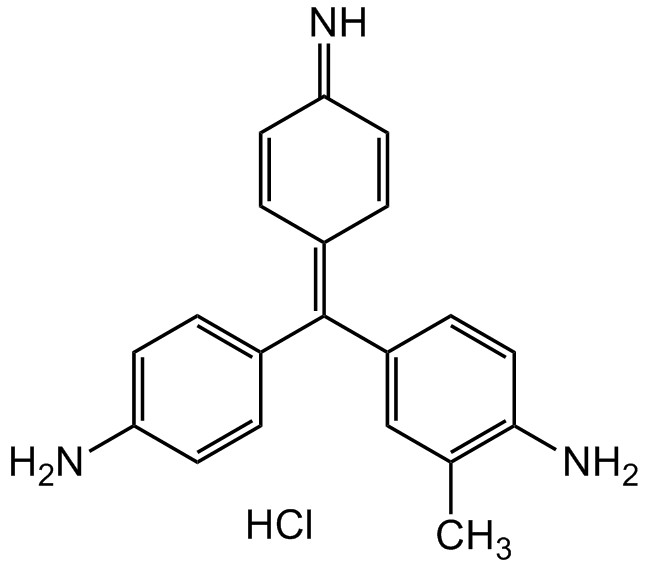
InChI=1S/C20H19N3.ClH/c1-13-12-16(6-11-19(13)23)20(14-2-7-17(21)8-3-14)15-4-9-18(22)10-5-15;/h2-12,21H,22-23H2,1H3;1H/b20-14-,21-17?;
InChiKey:
NIKFYOSELWJIOF-SVFFXJIWSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 632-99-5. Formula: C20H20ClN3. MW: 337.85. Gram's Fuchsin Solution is a reagent that could be used in qualitative procedures to differentiate gram-negative from gram-positive organisms. The Gram staining allows a fast differentiation of bacteria in Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The mureine structure of the bacteria walls is the basis of the color affinity. Bacteria will be stained with Gram's crystal violet solution - an aniline dye - in the first step. After the treatment with iod solution, a dye-iod complex will form. During the decolorizing step, this complex stays in the multilayer mureine structures of the Gram-positive bacteria and they will appear blue/violet. Gram-negative bacteria have a monolayer mureine structure only, the dye-iod complex does not stay bound to the cellwall, they will be decolorized. Gram-negative bacteria will be counterstained by Gram's Fuchsin solution and appear red/pink. Both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria pick up the counterstain. The counterstain, however, is unseen on Gram-positive bacteria because of the darker crystal violet stain.
MDL:
MFCD18071399
Molecular Formula:
C20H20ClN3
Molecular Weight:
337.85
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P201-P308 + P313
Product Description:
Gram's Fuchsin Solution is a reagent that could be used in qualitative procedures to differentiate gram-negative from gram-positive organisms. The Gram staining allows a fast differentiation of bacteria in Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The mureine structure of the bacteria walls is the basis of the color affinity. Bacteria will be stained with Gram's crystal violet solution - an aniline dye - in the first step. After the treatment with iod solution, a dye-iod complex will form. During the decolorizing step, this complex stays in the multilayer mureine structures of the Gram-positive bacteria and they will appear blue/violet. Gram-negative bacteria have a monolayer mureine structure only, the dye-iod complex does not stay bound to the cellwall, they will be decolorized. Gram-negative bacteria will be counterstained by Gram's Fuchsin solution and appear red/pink. Both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria pick up the counterstain. The counterstain, however, is unseen on Gram-positive bacteria because of the darker crystal violet stain.
SMILES:
NC1=CC=C(/C(C2=CC(C)=C(N)C=C2)=C3C=CC(C=C/3)=N)C=C1.Cl
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Fluorescent Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) E. Adams; Stain Technol. 50, 227 (1975) | (2) T.J. Beveridge; Biotech. Histochem. 76, 111 (2001) | (3) R. Coico, et al.; Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. Appendix 3-3C (2005)