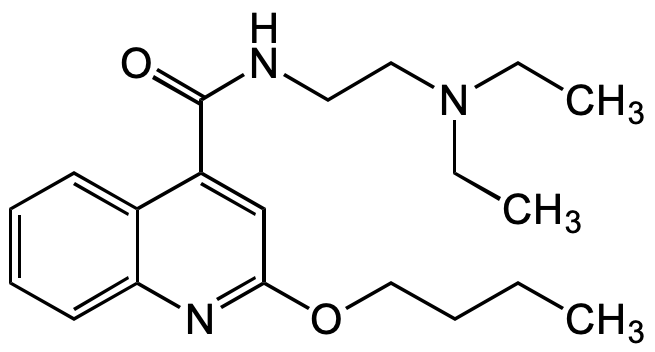
Cinchocaine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0694-G005 | 5 g | £59.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-C0694-G010 | 10 g | £102.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +4°C, Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Dibucaine; NSC 159055; 2-Butoxy-N-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)quinoline-4-carboxamide
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
85-79-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302-H315-H319-H332-H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C20H29N3O2/c1-4-7-14-25-19-15-17(16-10-8-9-11-18(16)22-19)20(24)21-12-13-23(5-2)6-3/h8-11,15H,4-7,12-14H2,1-3H3,(H,21,24)
InChiKey:
PUFQVTATUTYEAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 85-79-0. Formula: C20H29N3O2. MW: 343.46. Synthetic. Cinchocaine is an amide local anesthetic. It is among the most potent and toxic of the long-acting local anesthetics, by blocking sodium channels. Shown to be a calpain activator inducing platelet apoptosis and to induce apoptosis in leukemia cells. This compound can be used as a reference compound.
MDL:
MFCD00047595
Molecular Formula:
C20H29N3O2
Molecular Weight:
343.46
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P280-P305+P351+P338-P310
Product Description:
Cinchocaine is an amide local anesthetic. It is among the most potent and toxic of the long-acting local anesthetics, by blocking sodium channels. Shown to be a calpain activator inducing platelet apoptosis and to induce apoptosis in leukemia cells. This compound can be used as a reference compound.
Purity:
>97%
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
O=C(NCCN(CC)CC)C1=CC(OCCCC)=NC2=CC=CC=C21
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol, chloroform or DMSO. Insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) A. Fisher & R. Bryce-Smith; Anaesthesia 26, 324 (1971) | (2) K. Arita, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 905 (2000) | (3) H.A. Douglas, et al.; J. Neurophysiol. 105, 1482 (2011) | (4) W. Zhang, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 2125 (2011) | (5) K. Tonooka, et al.; Forensic Sci. Int. 265, 182 (2016)