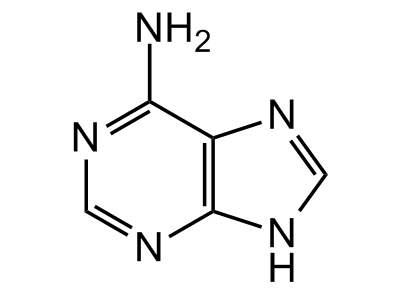
Adenine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-A0083-G025 | 25 g | £84.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-A0083-G100 | 100 g | £230.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
6-Aminopurine; Vitamin B4
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
73-24-5
Class:
6.1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS06
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C5H5N5/c6-4-3-5(9-1-7-3)10-2-8-4/h1-2H,(H3,6,7,8,9,10)
InChiKey:
GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 73-24-5. Formula: C5H5N5. MW: 135.13. Adenine is a purine nucleobase. It is part of DNA and RNA and is also a component of cofactors (NAD, FAD) and signaling molecules (cAMP). Adenine is essential for many in vivo and in vitro biochemical processes. Adenine is converted to adenosine with ribose. On phosphorylation, it forms AMP, ADP and ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is required during cellular metabolism. Adenine is metabolized to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine, which on accumulation in proximal tubules leads to the induction of chronic kidney disease (CKD) with severe anemia in rats. Adenine based derivatives elicit antiviral functionality against dsDNA viruses and are exploited for generating antiviral scaffolds. Adenine is suitable for use as a media nucleic acid base supplement in cell culture or food/dietary research.
MDL:
MFCD00041790
Molecular Formula:
C5H5N5
Molecular Weight:
135.13
Package Type:
Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P301 + P310
Product Description:
Adenine is a purine nucleobase. It is part of DNA and RNA and is also a component of cofactors (NAD, FAD) and signaling molecules (cAMP). Adenine is essential for many in vivo and in vitro biochemical processes. Adenine is converted to adenosine with ribose. On phosphorylation, it forms AMP, ADP and ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is required during cellular metabolism. Adenine is metabolized to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine, which on accumulation in proximal tubules leads to the induction of chronic kidney disease (CKD) with severe anemia in rats. Adenine based derivatives elicit antiviral functionality against dsDNA viruses and are exploited for generating antiviral scaffolds. Adenine is suitable for use as a media nucleic acid base supplement in cell culture or food/dietary research.
Purity:
>98% (NMR)
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble methanol or ethanol. Slightly soluble in water (~1mg/ml).
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
2811
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) G. Nuki; Ann. Rheum. Dis. 42, 8 (1983) | (2) R. Shapiro; Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 25, 83 (1995) | (3) J. Ross; J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 6987 (2006) | (4) T.E. Parry; Leuk. Res. 31, 1621 (2007) | (5) D. Thimm, et al.; Acta Physiol. 213, 808 (2015) | (6) C. Wang, et al.; Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 5, 431 (2015)