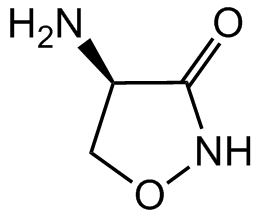
D-Cycloserine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-D0356-G001 | 1 g | £53.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-D0356-G005 | 5 g | £145.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term: +4°C, Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
(R)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidone; D-4-amino-3-isoxazolidone; D-Oxamycin; Seromycin; K300, NJ-21; (+)-Cycloserine; alpha-Cycloserine; (R)-Cycloserine; NSC 76029; NSC 154851
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
68-41-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C3H6N2O2/c4-2-1-7-5-3(2)6/h2H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
DYDCUQKUCUHJBH-UWTATZPHSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 68-41-7. Formula: C3H6N2O2. MW: 102.09. D-cycloserine (DCS) is an antibiotic, inhibiting cell-wall biosynthesis in bacteria. It is a tuberculostatic agent, that inhibits L-alanine racemase and D-alanine:D-alanine ligase, enzymes essential to peptidoglycan synthesis and bacterial cell wall formation. Formulations containing DCS have been used as second-line agents to treat drug resistant tuberculosis. A reason for limited use of this drug is the neurological side effects it causes, since it is able to penetrate into the central nervous system (CNS). DCS acts as a glutamatergic partial N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) agonist. It selectively binds at the glycine-binding site of the NMDA receptor and enable the opening of the NMDA channel. DCS has the ability to improve memory retention in senescence-accelerated mice which exhibit impaired learning and memory.
MDL:
MFCD00005353
Molecular Formula:
C3H6N2O2
Molecular Weight:
102.09
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
D-cycloserine (DCS) is an antibiotic, inhibiting cell-wall biosynthesis in bacteria. It is a tuberculostatic agent, that inhibits L-alanine racemase and D-alanine:D-alanine ligase, enzymes essential to peptidoglycan synthesis and bacterial cell wall formation. Formulations containing DCS have been used as second-line agents to treat drug resistant tuberculosis. A reason for limited use of this drug is the neurological side effects it causes, since it is able to penetrate into the central nervous system (CNS). DCS acts as a glutamatergic partial N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) agonist. It selectively binds at the glycine-binding site of the NMDA receptor and enable the opening of the NMDA channel. DCS has the ability to improve memory retention in senescence-accelerated mice which exhibit impaired learning and memory.
Purity:
>98% (TLC)
SMILES:
O=C1NOC[C@H]1N
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) W.F. Hood, et al.; Neurosci. Lett. 98, 91 (1989) | (2) G.B. Watson, et al.; Brain Res. 510, 158 (1990) | (3) J.F. Flood, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 221, 249 (1992) | (4) H. Baran, et al.; Brain Res. 652, 195 (1994) | (5) Z. Feng & R.G. Barletta; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 283 (2003) | (6) J.A. Caminero, et al.; Lancet Infect. Dis. 10, 621 (2010) | (7) W. Hong, et al.; Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 18, 691 (2014) (Review) | (8) S. Schade & W. Paulus; Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 19, pyv102 (2016) (Review)