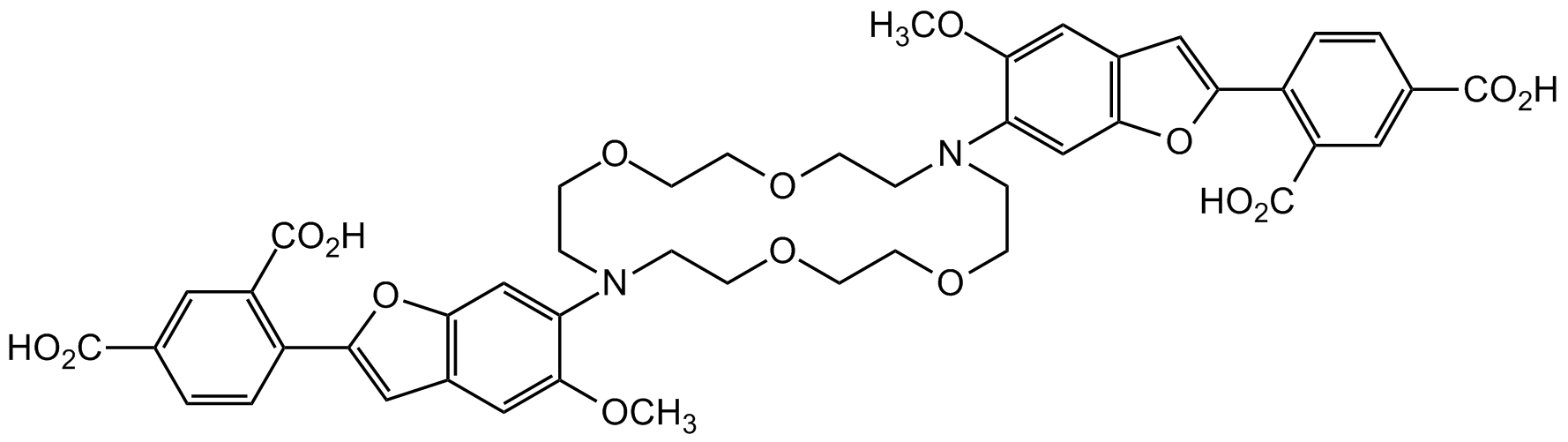
PBFI
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-P0662-M001 | 1 mg | £346.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short Term Storage: -20?C. Long Term Storage: -20?C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Potassium-binding Benzofuran Isophthalate
Appearance:
Brownish-yellow powder.
CAS:
124549-11-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C46H46N2O16/c1-57-41-23-29-21-39(31-5-3-27(43(49)50)19-33(31)45(53)54)63-37(29)25-35(41)47-7-11-59-15-17-61-13-9-48(10-14-62-18-16-60-12-8-47)36-26-38-30(24-42(36)58-2)22-40(64-38)32-6-4-28(44(51)52)20-34(32)46(55)56/h3-6,19-26H,7-18H2,1-2H3,(H,49,50)(H,51,52)(H,53,54)(H,55,56)
InChiKey:
YOQMJMHTHWYNIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 124549-11-7. Formula: C46H46N2O16. Molecular Weight: 882.86. PBFI is a cell-impermeant fluorescent indicator for potassium ions, suitable for detection of physiological concentrations of K+ in the presence of other monovalent cations. PBFI is used to measure intracellular potassium (K+) fluxes in animal cells and in plant cells and vacuoles. The observation that intracellular K+ levels are a controlling factor in apoptotic cell death pathways, increased the interest for PBFI. PBFI has been used for detecting adrenoceptor-stimulated decreases of intracellular K+ concentration in astrocytes and neurons, evaluating the mediating effects of K+ depletion on monocytic cell necrosis, measuring intracellular K+ fluxes associated with apoptotic cell shrinkage, monitoring mitochondrial KATP channel activation, or detecting elevated intracellular K+ levels associated with HIV-induced cytopathology. Flow cytometric measurements using UV argon-ion laser excitation (351nm and 364nm) of PBFI indicate that K+ efflux induces shrinkage of apoptotic cells and is a trigger for caspase activation. Spectral data: lambdaex 336nm;, lambdaem 557nm.
MDL:
MFCD00083473
Molecular Formula:
C46H46N2O16
Molecular Weight:
882.86
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
PBFI is a cell-impermeant fluorescent indicator for potassium ions, suitable for detection of physiological concentrations of K+ in the presence of other monovalent cations. PBFI is used to measure intracellular potassium (K+) fluxes in animal cells and in plant cells and vacuoles. The observation that intracellular K+ levels are a controlling factor in apoptotic cell death pathways, increased the interest for PBFI. PBFI has been used for detecting adrenoceptor-stimulated decreases of intracellular K+ concentration in astrocytes and neurons, evaluating the mediating effects of K+ depletion on monocytic cell necrosis, measuring intracellular K+ fluxes associated with apoptotic cell shrinkage, monitoring mitochondrial KATP channel activation, or detecting elevated intracellular K+ levels associated with HIV-induced cytopathology. Flow cytometric measurements using UV argon-ion laser excitation (351nm and 364nm) of PBFI indicate that K+ efflux induces shrinkage of apoptotic cells and is a trigger for caspase activation. Spectral data: lambdaex 336nm;, lambdaem 557nm.
Purity:
~80% (HPLC)
SMILES:
COC1=CC2=C(OC(C3=C(C(O)=O)C=C(C(O)=O)C=C3)=C2)C=C1N4CCOCCOCCN(C5=CC(OC(C6=C(C(O)=O)C=C(C(O)=O)C=C6)=C7)=C7C=C5OC)CCOCCOCC4
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in methanol or DMSO.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) P. Jezek, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 265, 10522 (1990) | (2) S.E. Kasner & M.B. Ganz; Am. J. Physiol. 262, F462 (1992) | (3) K. Venema, et al. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1146, 87 (1993) | (4) R. Crossley, et al.; J. Chem. Soc. Perk. Trans. 2, 513 (1994) | (5) K. Meuwis; Biophys. J. 68, 2469 (1995) | (6) H. Muyderman, et al.; Neurochem. Int. 38, 269 (2001) | (7) A.L. Cook, et al.; Cell Signal. 14, 1023 (2002) | (8) S.J. Halperin & J.P. Lynch; J. Exp. Bot. 54, 2035 (2003) | (9) D. Liu, et al.; J. Neurochem. 86, 966 (2003) | (10) A.D. Costa, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290, H406 (2006) | (11) P. Andersson, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 20, 986 (2006) | (12) S. Jorgensen, et al.; Methods Mol. Biol. 491, 257 (2008) | (13) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010) | (14) C.S. Arlehamn, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 10508 (2010)