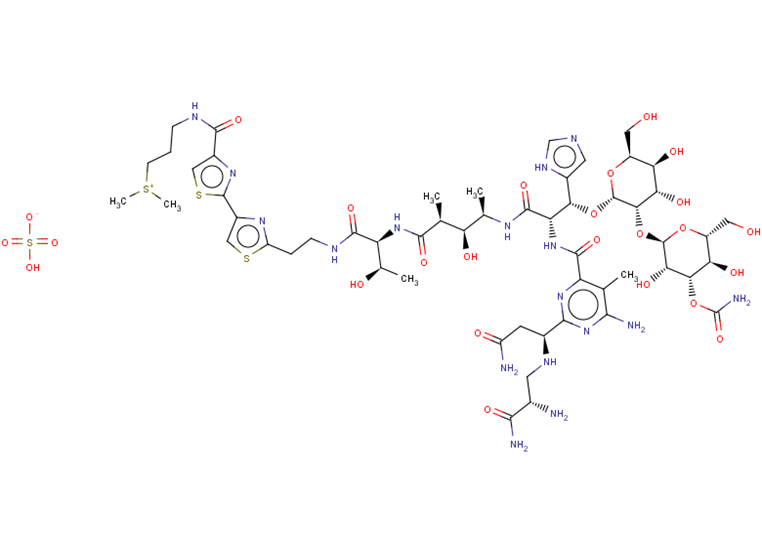
Bleomycin Sulfate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T6116-2mg | 2mg | £111.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T6116-5mg | 5mg | £130.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T6116-10mg | 10mg | £170.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T6116-1mL | 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | £287.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T6116-25mg | 25mg | £287.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T6116-50mg | 50mg | £435.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T6116-100mg | 100mg | £470.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Bleomycin Sulfate, a glycopeptide antibiotic, is an anticancer agent for squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). In UT-SCC-19A cells, the IC50 of Bleomycin Sulfate is 4 nM.
CAS:
9041-93-4
Formula:
C55H85N17O25S4
Molecular Weight:
1512.62
Pathway:
DNA Damage/DNA Repair; Cell Cycle/Checkpoint; Microbiology/Virology
Purity:
0.9973
SMILES:
OS([O-])(=O)=O.C[C@@H](O)[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)c1nc(nc(N)c1C)[C@H](CC(N)=O)NC[C@H](N)C(N)=O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]1O[C@@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC(N)=O)[C@@H]1O)c1cnc[nH]1)C(=O)NCCc1nc(cs1)-c1nc(cs1)C(=O)NCCC[S+](C)C
Target:
DNA/RNA Synthesis; Antibiotic
References
Wang T, Shi S, Shi Y, et al.Chemical-induced phase transition and global conformational reorganization of chromatin.Nature Communications.2023, 14(1): 5556.
Liang J, Niu Z, Zhang B, et al. Liang J, Niu Z, Zhang B, et al. p53-dependent elimination of aneuploid mitotic offspring by entosis[J]. Cell Death & Differentiation. 2020: 1-15.
Cort A, et al. Mol Med Report. 2012, 5(6), 1481-1486.
Liang J, Niu Z, Yu X, et al. Counteracting Genome Instability by p53-dependent Mintosis[J]. bioRxiv. 2020.
Denholm EM, et al. Am J Pathol. 1989, 134(2), 355-363.
Yi X M, Li M, Chen Y D, et al. Reciprocal regulation of IL-33 receptor?mediated inflammatory response and pulmonary fibrosis by TRAF6 and USP38. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2022, 119(10): e2116279119
Banerjee ER, et al. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012, 3(3), 21.
J??skel?-Saari HA, et al. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1997;529:241-4.
Liang J, Niu Z, Zhang B, et al Liang J, Niu Z, Zhang B, et al. p53-dependent elimination of aneuploid mitotic offspring by entosis. Cell Death & Differentiation. 2020: 1-15.
Corboz MR, et al. Therapeutic?administration?of?inhaled?INS1009, a?treprostinil?prodrug?formulation,?inhibits?bleomycin-induced?pulmonary?fibrosis?in?rats. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.?2018 Apr;49:95-103.
Zongwang Zhang1,2 , Yanwei Wu2 , Bing Wu2,3, etal, Lili Niu1* and Wei Tang2,3. DZ2002 ameliorates fibrosis, inflammation,and vasculopathy in experimental systemic sclerosis models. Arthritis Research & Therapy. (2019) 21:290
Paviolo NS, et al. Mutat Res. 2012, 734(1-2), 5-11.
Hovhannisyan G, et al. Comparative analysis of individual chromosome involvement in micronuclei induced by bleomycin in human leukocytes. Mol Cytogenet. 2016 Jun 21;9:49.
Liang J, Niu Z, Zhang B, et al. p53-dependent elimination of aneuploid mitotic offspring by entosis. Cell Death & Differentiation. 2020: 1-15