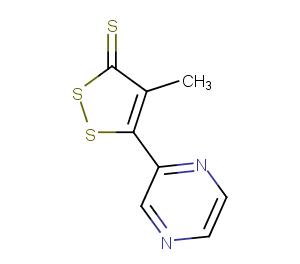
Oltipraz
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T0153-5mg | 5mg | £95.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T0153-1mL | 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | £111.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T0153-10mg | 10mg | £111.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T0153-25mg | 25mg | £128.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T0153-50mg | 50mg | £142.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T0153-100mg | 100mg | £172.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T0153-200mg | 200mg | £200.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Oltipraz is a synthetic dithiolethione with potential chemopreventive and anti-angiogenic properties. Oltipraz induces phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S transferase (GST) and NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). The induction of detoxification enzymes enhances the detoxification of certain cancer-causing agents, thereby enhancing their elimination and preventing carcinogen-induced DNA damages. Although the exact mechanism through which the anti-angiogenesis effect remains to be fully elucidated, oltipraz maybe able to modulate the expression of a number of angiogenic factors, thereby blocking the sustained and focal neovascularization in multiple tumor cell types.
CAS:
64224-21-1
Formula:
C8H6N2S3
Molecular Weight:
226.33
Pathway:
Proteases/Proteasome; Chromatin/Epigenetic; Microbiology/Virology; Metabolism; Immunology/Inflammation; Angiogenesis
Purity:
0.9956
SMILES:
Cc1c(ssc1=S)-c1cnccn1
Target:
HIF/HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase; HIV Protease; Reverse Transcriptase; Nrf2; HIF
References
1. Ramos-Gomez M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001, 98(6), 3410-3415..
2. Lee WH, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009, 8(10), 2791-2802.
3. Shimozono R, et al. Mol Pharmacol. 2013, 84(1), 62-70.