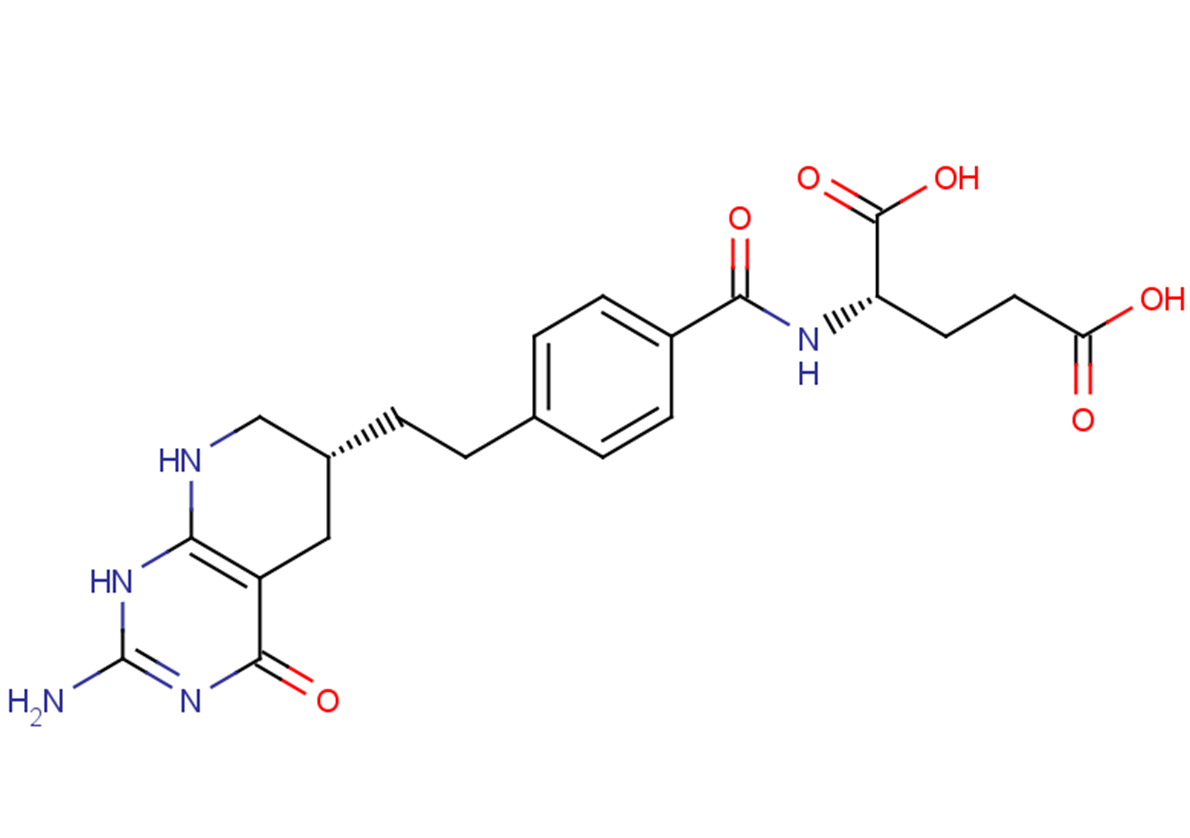
Lometrexol
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T15826-1mg | 1mg | £149.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T15826-5mg | 5mg | £259.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T15826-1mL | 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | £290.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T15826-10mg | 10mg | £346.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T15826-25mg | 25mg | £536.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T15826-50mg | 50mg | £736.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T15826-100mg | 100mg | £994.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Lometrexol has anticancer activity. Lometrexol can further inhibit de novo purine synthesis, causing abnormal cell proliferation and apoptosis, even cell cycle arrest. Lometrexol is an antipurine antifolate, can inhibit the activity of glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT) by tightly binding with it .
CAS:
106400-81-1
Formula:
C21H25N5O6
Molecular Weight:
443.46
Pathway:
Metabolism|Cell Cycle/Checkpoint|DNA Damage/DNA Repair
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
Nc1nc2NC[C@H](CCc3ccc(cc3)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)Cc2c(=O)[nH]1
Target:
DHFR
References
Xu L, et al. The effect of inhibiting glycinamide ribonucleotide formyl transferase on the development of neural tube in mice. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016 Aug 23;13(1):56.
Scaletti E, et, al. Structural basis of inhibition of the human serine hydroxymethyltransferase SHMT2 by antifolate drugs. FEBS Lett. 2019 Jul;593(14):1863-1873.
Bronder JL, et, al. Antifolates targeting purine synthesis allow entry of tumor cells into S phase regardless of p53 function. Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 15;62(18):5236-41.