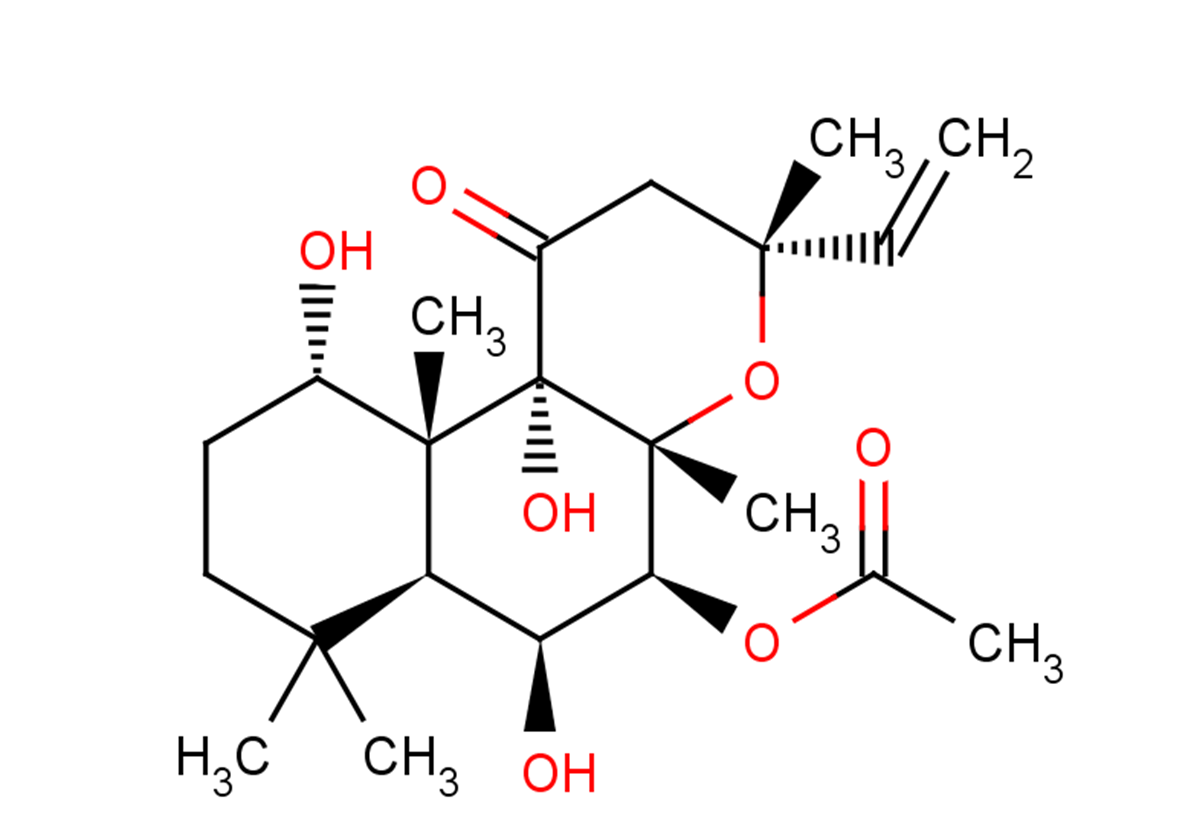
Forskolin
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T2939-5mg | 5mg | £100.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T2939-10mg | 10mg | £115.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T2939-50mg | 50mg | £148.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T2939-100mg | 100mg | £189.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T2939-200mg | 200mg | £226.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Forskolin, a potent activator of the adenylate cyclase (EC50: 0.5 μM), can increase the cAMP level. It is extracted from the plant Coleus forskohlii.
Biological Applications:
Natural forskolin is primarily extracted from the root tissues of the plant Coleus forskohlii and holds significant medicinal value. It is known to exhibit favorable pharmacological activities in areas such as anti-cancer, anti-viral, anti-asthmatic, anti-hypertensive, and cardiac strengthening. As a cAMP activator, it has been used as a valuable tool to reveal the significance of cAMP in various cellular events across different organs, potentially providing more therapeutic targets for treating diseases.
In the cardiovascular system, the cAMP signaling pathway plays a role in regulating processes such as heart contraction and relaxation. In the nervous system, the activation of the cAMP signaling pathway can promote synaptic transmission in neurons and enhance memory formation. In metabolic-related diseases like diabetes and obesity, the regulatory effects of the cAMP signaling pathway are associated with insulin secretion and energy metabolism.
The cAMP signaling pathway also plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system. In T cells, the activation of the cAMP signaling pathway inhibits cell activation, contributing to immune tolerance. In macrophages, the activation of the cAMP signaling pathway suppresses the production of nitric oxide, serving as an anti-inflammatory effect.
CAS:
66575-29-9
Description:
Forskolin, a potent activator of the adenylate cyclase (EC50: 0.5 uM), can increase the cAMP level. It is extracted from the plant Coleus forskohlii.
Formula:
C22H34O7
Mechanism of Action:
Forskolin, as a direct, rapid, and reversible activator of adenylate cyclase, increases cellular cAMP levels. Intracellular cAMP serves as a secondary messenger involved in various physiological processes such as cell differentiation, proliferation, metabolic regulation, and inflammatory responses. The known signaling pathways of cAMP primarily transmit signals through the activation of protein kinase A (PKA). cAMP molecules can bind to two cAMP-binding domains in the subunits of PKA, releasing its two subunits, activating PKA, and phosphorylating downstream target proteins. Additionally, the cAMP signaling pathway includes membrane receptors (ion channels), Epac, and others. The cAMP signaling pathway plays a crucial role in maintaining normal physiological functions, growth and development processes, metabolic regulation, and inflammatory responses.
Molecular Weight:
410.507
Pathway:
Neuroscience; Metabolism; Autophagy
Purity:
0.9986
Research Area:
Nervous System; Stem Cell Research; Cell Regulation; Growth and Development Processes; Metabolic Regulation; Inflammation; Anti-cancer; Antihypertensive; Anti-Asthma; Cardiac Strengthening
SMILES:
CC(=O)O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H]2C(C)(C)CC[C@H](O)[C@]2(C)[C@@]2(O)C(=O)C[C@@](C)(O[C@]12C)C=C
Target:
FXR; Adenylyl cyclase; AChR; Autophagy
References
1. Robbins JD, et al. Forskolin carbamates: binding and activation studies with type I adenylyl cyclase. J Med Chem. 1996 Jul 5;39(14):2745-52.
10. Xiaoli F, Yaqing Z, Ruhui L, et al. Graphene oxide disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis through inducing intracellular redox deviation and autophagy-lysosomal network dysfunction in SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2021: 126158.
2. Rodriguez G, et al. Forskolin-inducible cAMP pathway negatively regulates T-cell proliferation by uncoupling the interleukin-2 receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):7137-46.
3. Hou P, et al. Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds. Science. 2013 Aug 9;341(6146):651-4.
4. Matsumiya W, et al. Forskolin modifies retinal vascular development in Mrp4-knockout mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Dec 7;53(13):8029-35.
5. El-Agroudy NN, et al. Forskolin, a hedgehog signalling inhibitor, attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;173(22):3248-3260.
6. Lu J, Dou F, Yu Z. The potassium channel KCa3. 1 represents a valid pharmacological target for microgliosis-induced neuronal impairment in a mouse model of Parkinson?s disease[J]. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2019, 16(1): 1-14.
7. Lin J Y, Cheng J, Du Y Q, et al. In vitro expansion of pancreatic islet clusters facilitated by hormones and chemicals[J]. Cell Discovery. 2020, 6(1): 1-12.
8. Lin J Y, Cheng J, Du Y Q, et al. In vitro pancreatic islet cluster expansion facilitated by hormones and chemicals[J]. Cell Discovery. 2020, 6(1): 1-12.
9. Wu L, Dong A, Dong L, et al. PARIS, an optogenetic method for functionally mapping gap junctions[J]. eLife. 2019 Jan 14;8. pii: e43366.