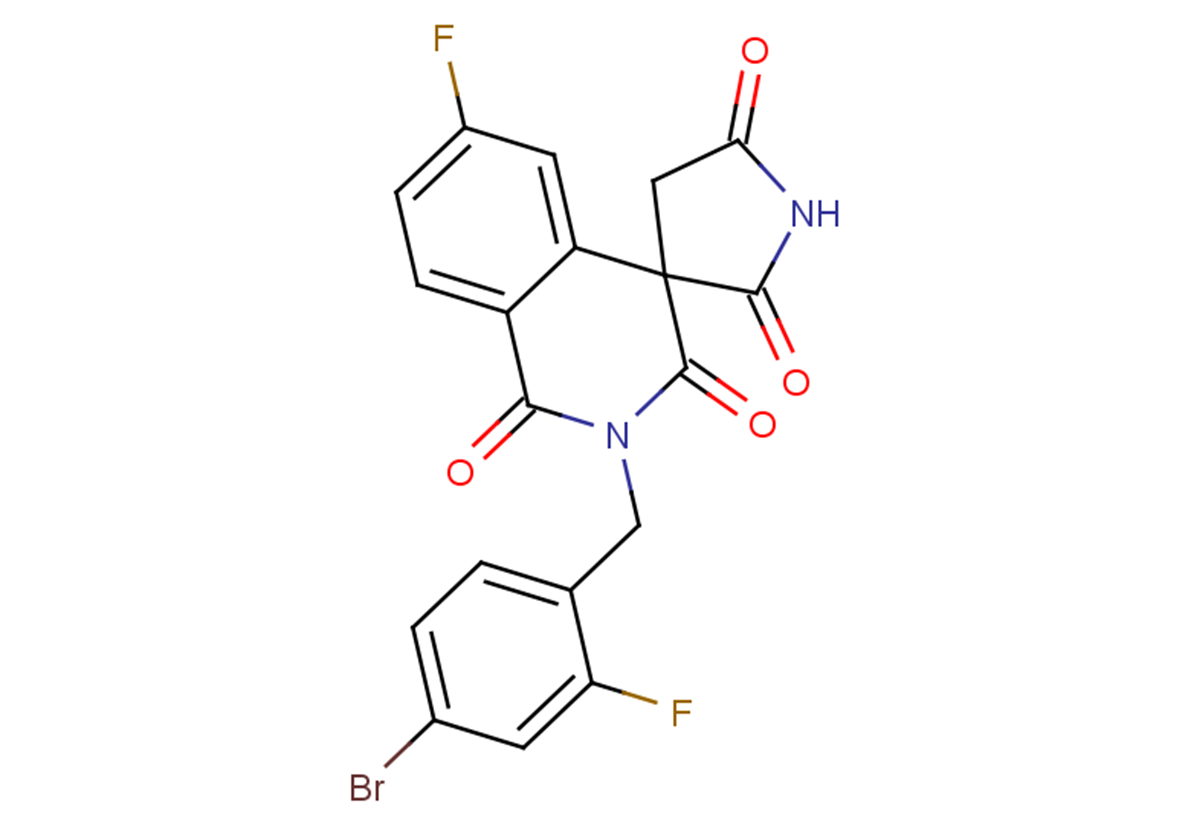
Minalrestat
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T33389-1mg | 1mg | £278.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T33389-5mg | 5mg | £586.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T33389-10mg | 10mg | £804.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T33389-25mg | 25mg | £1,171.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T33389-50mg | 50mg | £1,556.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Minalrestat (ARI-509, WAY-121509, WAY-ARI-509, Wayari-509) is an aldose reductase inhibitor that can correct impaired microvascular reactivity in diabetes.
CAS:
129688-50-2
Formula:
C19H11BrF2N2O4
Molecular Weight:
449.208
Pathway:
Metabolism|Endocrinology/Hormones
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
Fc1ccc2C(=O)N(Cc3ccc(Br)cc3F)C(=O)C3(CC(=O)NC3=O)c2c1
Target:
Reductase
References
Akamine EH, et al. Minalrestat, an aldose reductase inhibitor, corrects the impaired microvascular reactivity in diabetes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Mar;304(3):1236-42.
Cruz JW, et al. Minalrestat and leukocyte migration in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2003 May-Jun;19(3):223-31.
Tse SY, et al. Determination of minalrestat (an aldose reductase inhibitor) in rat, dog and human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1998 May 8;709(1):127-35.
El-Kabbani O, et al. Ultrahigh resolution drug design. II. Atomic resolution structures of human aldose reductase holoenzyme complexed with Fidarestat and Minalrestat: implications for the binding of cyclic imide inhibitors. Proteins. 2004 Jun 1;55(4):805-13.
Kapor-Drezgic J, et al. Effect of high glucose on mesangial cell protein kinase C-delta and -epsilon is polyol pathway-dependent. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Jun;10(6):1193-203.