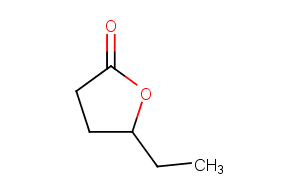
γ-Hexalactone
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T8098-1g | 1g | £104.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T8098-1mL | 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | £107.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Gamma-Caprolactone, also known as 4-ethyl-4-butanolide or 4-hexanolide, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as gamma butyrolactones. Gamma butyrolactones are compounds containing a gamma butyrolactone moiety, which consists of an aliphatic five-member ring with four carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and bears a ketone group on the carbon adjacent to the oxygen atom. Thus, Gamma-caprolactone is considered to be a fatty ester lipid molecule. Gamma-Caprolactone is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. Gamma-Caprolactone exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. Outside of the human body, Gamma-caprolactone has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as potato, cereals and cereal products, pomes, alcoholic beverages, and fruits. This could make Gamma-caprolactone a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. 4-hydroxy-Hexanoic acid gamma-lactone is occasionally found as a volatile component of human urine. In some cases differences up to an order of magnitude are observed. 4-hydroxy-Hexanoic acid gamma-lactone has been found in the polar fraction of human blood. Biological fluids such as blood and urine have been shown to contain a large number of components, some of them volatiles (low boiling point) apparently present in all individuals, while others such are much more variable. Although some of these changes may have dietary origins, others seem to be characteristic of the individual.
CAS:
695-06-7
Formula:
C6H10O2
Molecular Weight:
114.144
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
CCC1CCC(=O)O1
References
Bianchi T, et al. Investigation of the aroma of commercial peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) types by Proton Transfer Reaction-Mass Spectrometry (PTR-MS) and sensory analysis. Food Res Int. 2017 Sep;99(Pt 1):133-146.
E-Nose and GC-MS Reveal a Difference in the Volatile Profiles of White- and Red-Fleshed Peach Fruit. Sensors (Basel). 2018 Mar 2;18(3).
Shangula S, et al. PON1 increases cellular DNA damage by lactone substrates. Arch Toxicol. 2019 Jul;93(7):2035-2043.