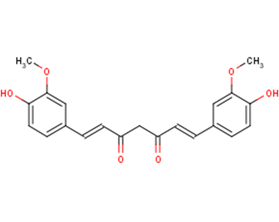
Curcumin
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T1516-25mg | 25mg | £95.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T1516-50mg | 50mg | £101.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T1516-1mL | 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | £111.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T1516-100mg | 100mg | £111.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T1516-200mg | 200mg | £116.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T1516-500mg | 500mg | £141.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Curcumin is a phytopolylphenol pigment isolated from the plant Curcuma longa, commonly known as turmeric, with a variety of pharmacologic properties. Curcumin blocks the formation of reactive oxygen species, possesses anti-inflammatory properties as a result of inhibition of cyclooxygenases (COX) and other enzymes involved in inflammation; and disrupts cell signal transduction by various mechanisms including inhibition of protein kinase C. These effects may play a role in the agent's observed antineoplastic properties, which include inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and suppression of chemically induced carcinogenesis and tumor growth in animal models of cancer.
CAS:
458-37-7
Formula:
C21H20O6
Molecular Weight:
368.39
Pathway:
Cell Cycle/Checkpoint; Apoptosis; Chromatin/Epigenetic; Microbiology/Virology; Immunology/Inflammation; Autophagy
Purity:
0.9751
SMILES:
COc1cc(ccc1O)C=CC(=O)CC(=O)C=Cc1ccc(O)c(OC)c1
Target:
Mitophagy; Epigenetic Reader Domain; Ferroptosis; Influenza Virus; Nrf2; Histone Acetyltransferase; Autophagy
References
1. Gao S, et al. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013, 59:739-47.
10. Tian D, Cao L, Li Q, et al. Benzannulated 5, 5-spiroketal sesquiterpenes from the roots of Angelica Pubescens[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2021, 107: 104604.
2. Nasiri M, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013, 14(6):3449-3453.
3. Cao A, et al. Apoptosis. 2013, 18(11):1391-1402.
4. Jiang H, et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013, 47:33-39.
5. Odot J, et al. Int J Cancer. 2004, 111(3):381-387.
6. Lu J, Lu Z, Liu L, et al. Identification of crocin as a new hIAPP amyloid inhibitor via a simple yet highly biospecific screening system[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity. 2021
7. Zhou H, Ning Y, Zeng G, et al. Curcumin promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells by inactivating AKT[J]. Oncology Reports. 2021, 45(4): 1-1.
8. Sun L, Qian S, Ma Y, et al. Iron Overload Adversely Effects Bone Marrow Haematogenesis via SIRT-SOD2-MROS in a Process Ameliorated by Curcumin[J]. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters. 2021, 26(1): 1-15.
9. Geng W, Guo X, Zhang L, et al. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of multiple myeloma cells via NEAT1-mediated Wnt/?-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2018 Nov;107:484-494.