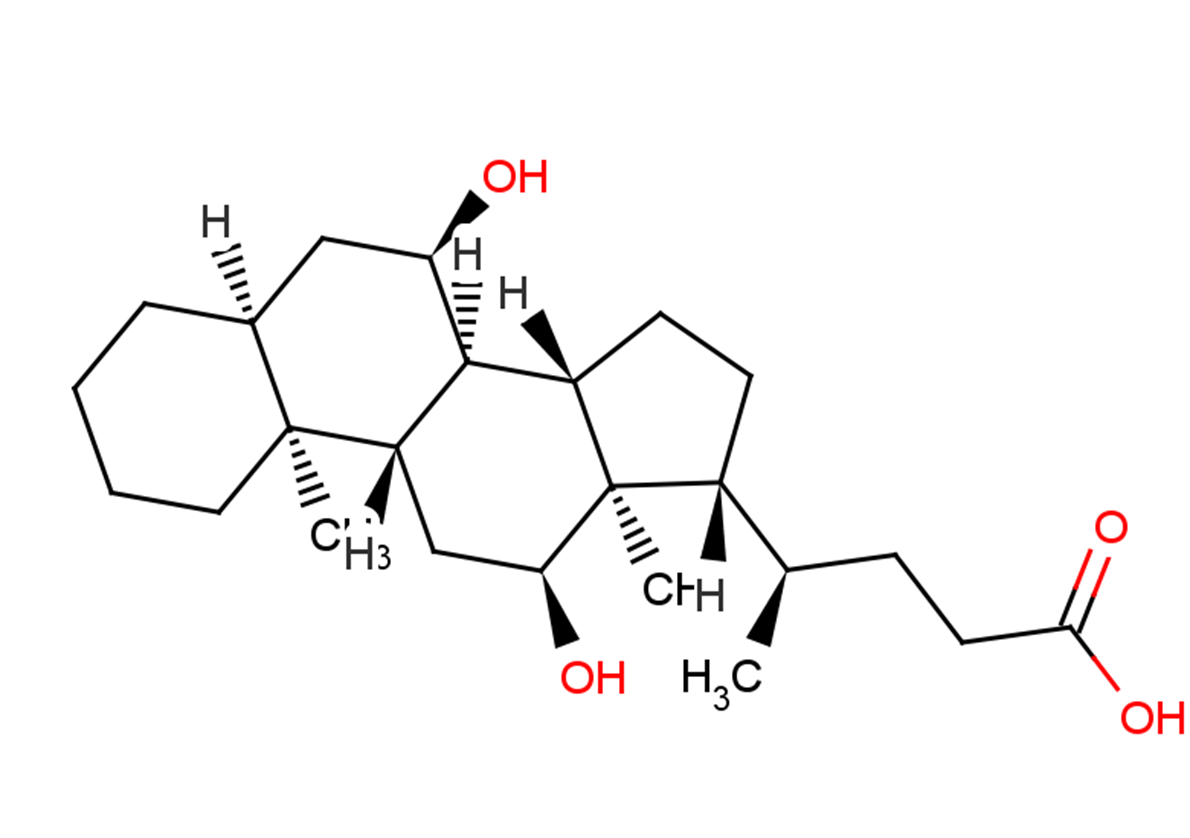
Isodeoxycholic Acid
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T36585-1mg | 1mg | £115.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T36585-5mg | 5mg | £229.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T36585-10mg | 10mg | £329.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T36585-25mg | 25mg | £570.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T36585-50mg | 50mg | £777.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T36585-100mg | 100mg | £1,018.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Isodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid that is formed via epimerization of deoxycholic acid by intestinal bacteria.[1] It has a greater critical micelle concentration than DCA, indicating reduced detergent activity, and is less active than DCA in inhibiting growth in a panel of seven gut commensal bacteria species. Isodeoxycholic acid (0.1%) inhibits spore germination induced by taurocholic acid in several C. difficile strains, as well as decreases the cytotoxicity of C. difficile culture supernatants to Vero cells.[2] Plasma levels of isodeoxycholic acid are decreased in a rat model of high-fat diet-induced obesity compared with rats fed a normal diet.[3]
CAS:
566-17-6
Formula:
C24H40O4
Molecular Weight:
392.6
Pathway:
Membrane transporter/Ion channel|Microbiology/Virology
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
C[C@@]12[C@@](C[C@@H](O)[C@]3([H])[C@]2([H])C[C@H](O)[C@@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]4([H])[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O)([H])CCCC1
Target:
Chloride channel|Antibacterial
References
Lin H, et al. Alterations of Bile Acids and Gut Microbiota in Obesity Induced by High Fat Diet in Rat Model. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(13):3624-3632.
Devlin AS, et al. A biosynthetic pathway for a prominent class of microbiota-derived bile acids. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11(9):685-690.
Takei H, et al. Characterization of long-chain fatty acid-linked bile acids: a major conjugation form of 3?-hydroxy bile acids in feces. J Lipid Res. 2022;63(10):100275.
Thanissery R, et al. Inhibition of spore germination, growth, and toxin activity of clinically relevant C. difficile strains by gut microbiota derived secondary bile acids. Anaerobe. 2017;45:86-100.