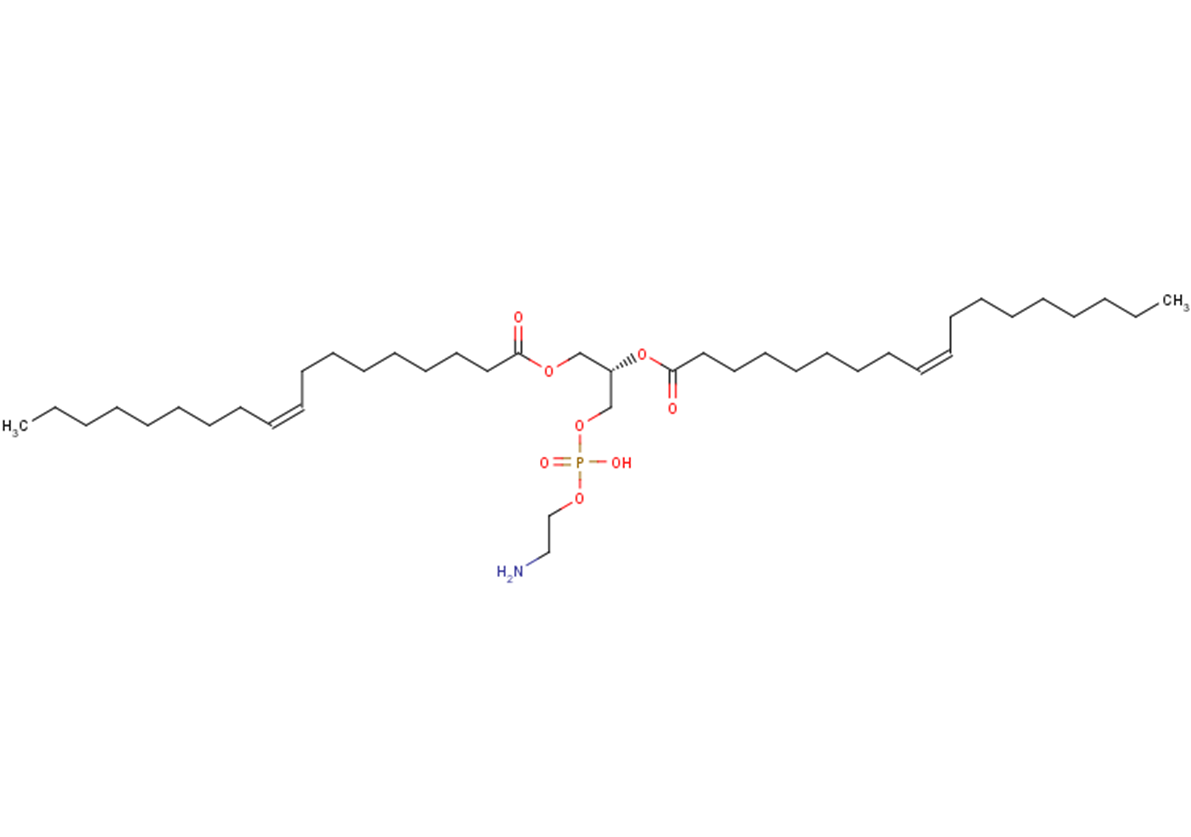
Phosphatidylethanolamines (egg)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T38141-500mg | 500mg | £103.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids. In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone. It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA. Phosphatidylethanolamines (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
CAS:
39382-08-6
Formula:
C41H78NO8P
Molecular Weight:
744.048
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
CCCCCCCCC=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OCCN)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=C/CCCCCCCC
References
Wood PL, et al. Lipidomics of the chicken egg yolk: high-resolution mass spectrometric characterization of nutritional lipid families. Poult Sci. 2021;100(2):887-899.
Wang Y, et al. Quantitative lipidomic analysis of chicken egg yolk during its formation. J Sci Food Agric. 2023;103(8):3997-4005.