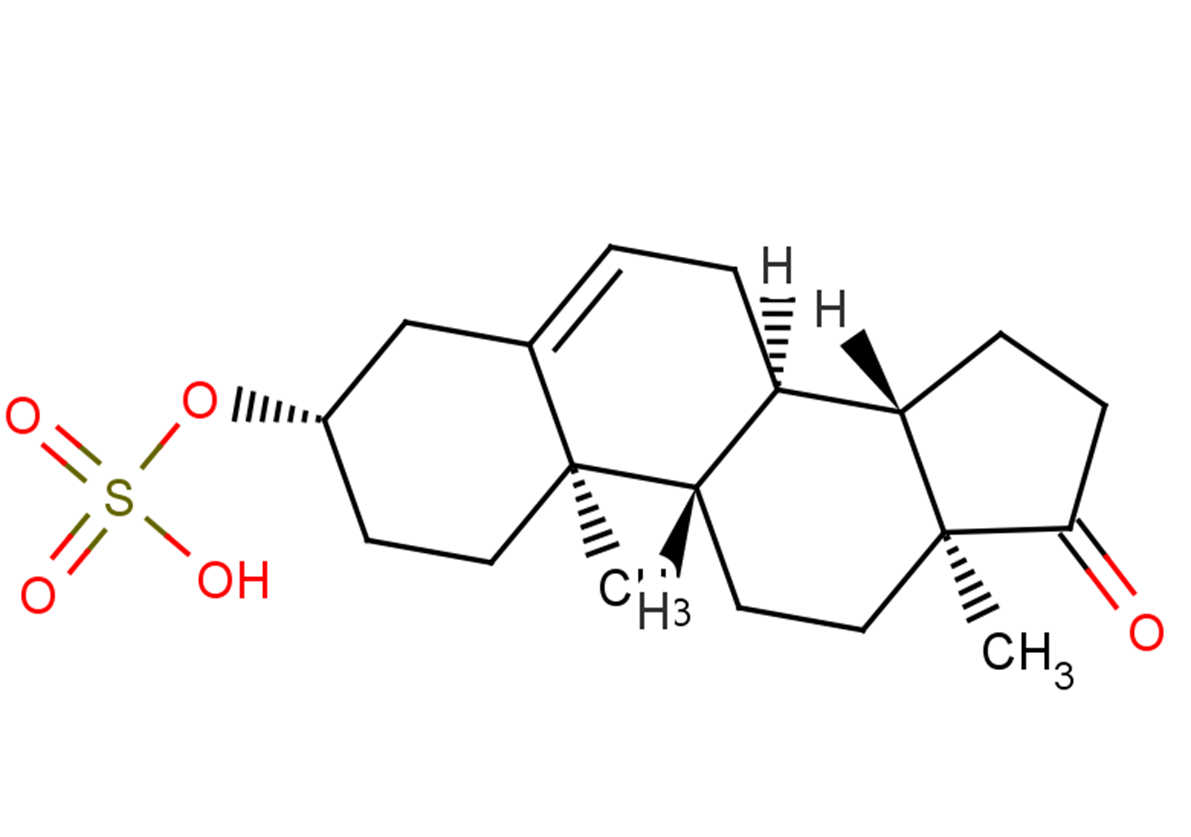
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T26366-1mg | 1mg | £103.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T26366-5mg | 5mg | £142.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T26366-1mL | 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | £148.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T26366-10mg | 10mg | £189.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T26366-25mg | 25mg | £309.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T26366-50mg | 50mg | £450.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T26366-100mg | 100mg | £625.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate influences the migration of neurons, arborization of dendrites, and formation of new synapses.
CAS:
651-48-9
Formula:
C19H28O5S
Molecular Weight:
368.49
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
C[C@@]12[C@@]3([C@]([C@]4([C@](C)(CC3)C(=O)CC4)[H])(CC=C1C[C@@H](OS(=O)(=O)O)CC2)[H])[H]
References
1. do Vale S, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS) and emotional processing - A behavioral and electrophysiological approach. Horm Behav. 2015 Jul;73:94-103.
2. E E Baulieu, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) as neuroactive neurosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 14;95(8):4089-91.
3. C R Parker Jr, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate production in the human adrenal during development and aging. Steroids. 1999 Sep;64(9):640-7.
4. Stuart W Hoffman, et al. The delayed administration of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate improves recovery of function after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2003 Sep;20(9):859-70.