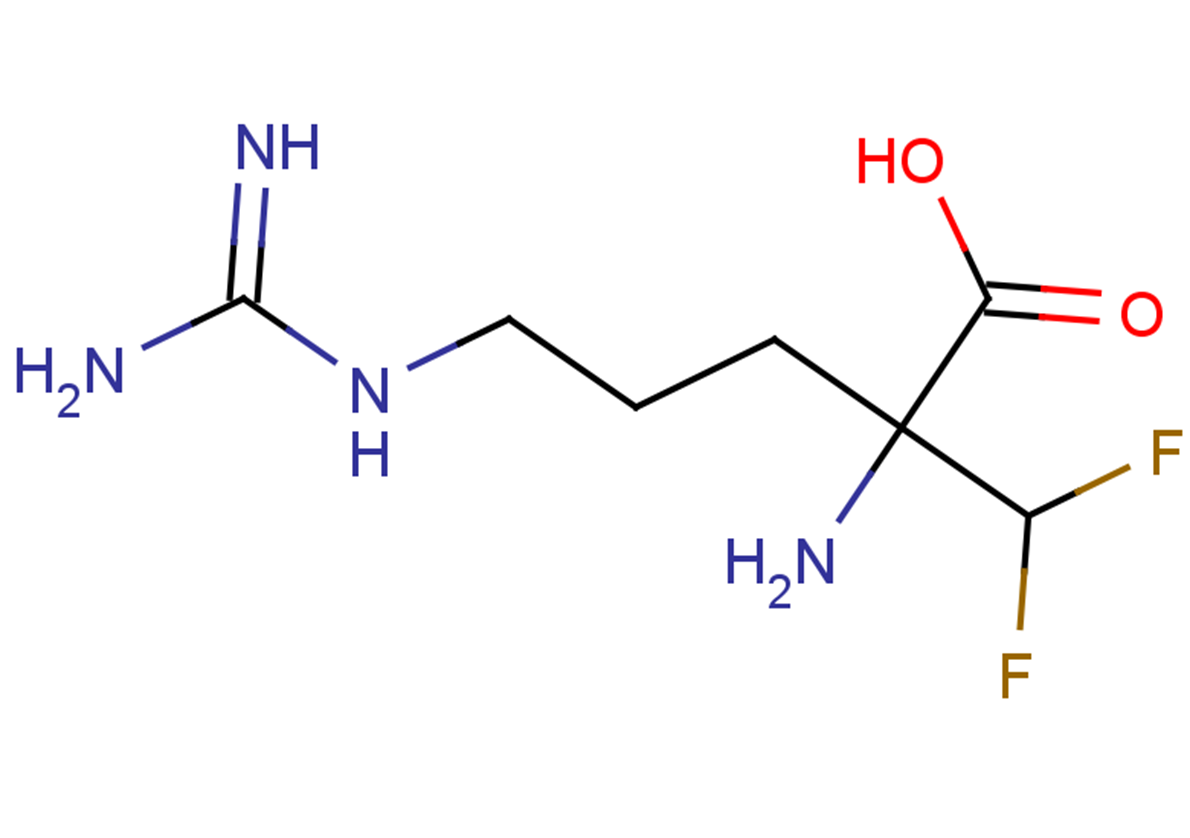
α-(difluoromethyl)-DL-Arginine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T35449-1mg | 1mg | £129.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T35449-5mg | 5mg | £239.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T35449-10mg | 10mg | £345.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T35449-25mg | 25mg | £480.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T35449-50mg | 50mg | £664.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T35449-100mg | 100mg | £863.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
| TAR-T35449-500mg | 500mg | £1,661.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Bacteria synthesize the cellular growth factor putrescine through a number of pathways. One pathway involves the decarboxylation of arginine by arginine decarboxylase to produce agmatine, which is then degraded to putrescine. While important for various cellular processes (e.g., cell division, differentiation, environmental stress responses) in all living organisms, including plants, high levels of this polyamine can be toxic.[1] α-(difluoromethyl)-DL-Arginine (DFMA) is an enzyme-activated, irreversible inhibitor of the arginine decarboxylases of E. coli (Ki = 800 μM), P. aeruginosa, and K. pneumoniae.[2] At 0.01 mM, it has been shown to prevent the osmotic stress-induced increase in arginine decarboxylase activity and putrescine synthesis in oat leaf cells.[3],[4] DFMA can also reduce the growth of T. cruzi in mammalian host cells at a minimal concentration of 10 mM and prevent the growth of C. parvum in a T cell receptor alpha-deficient mouse model when combined with various polyamine analogs.[5],[6]
CAS:
69955-43-7
Formula:
C7H14F2N4O2
Molecular Weight:
224.212
Purity:
0.98
SMILES:
NC(N)=NCCCC(N)(C(F)F)C(O)=O
References
A Kallio, et al. DL-?-(Difluoromethyl)arginine: A potent enzyme-activated irreversible inhibitor of bacterial decarboxylases. Biochemistry 20(11), 3163-3168 (1981).
Flores, H.E, et alPolyamines and plant stress: Activation of putrescine biosynthesis by osmotic shock. Science 217(4566), 1259-1261 (1982).
Kierszenbaum, F, et al. Arginine decarboxylase inhibitors reduce the capacity of Trypanosoma cruzi to infect and multiply in mammalian host cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 84(12), 4278-4282 (1987).
Nigel Yarlett, et al. Activities of DL-?-difluoromethylarginine and polyamine analogues against Cryptosporidium parvum infection in a T-cell receptor ?-deficient mouse model. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 51(4), 1234-1239 (2007).
Gill, S.S., et al. Polyamines and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 5(1), 26-33 (2010).
Tiburcio, A.F, et al. Polyamine metabolism and osmotic stress. II. Improvement of oat protoplasts by an inhibitor of arginine decarboxylase. Plant Physiology 82, 375-378 (1986).