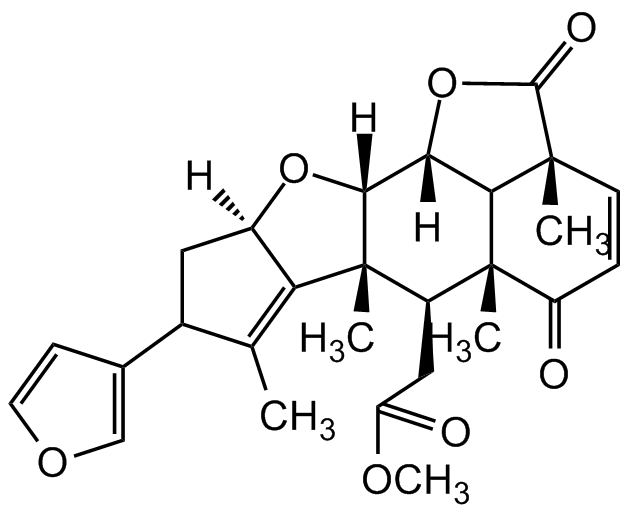
Nimbolide
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-N0360-M005 | 5 mg | £219.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short term: -20°C. Long term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
NSC 309909
Appearance:
White to faint yellow powder.
CAS:
25990-37-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C27H30O7/c1-13-15(14-7-9-32-12-14)10-16-20(13)27(4)17(11-19(29)31-5)26(3)18(28)6-8-25(2)22(26)21(23(27)33-16)34-24(25)30/h6-9,12,15-17,21-23H,10-11H2,1-5H3/t15?,16-,17-,21-,22?,23-,25-,26+,27-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
JZIQWNPPBKFOPT-FTCZZEDLSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 25990-37-8. Formula: C27H30O7. MW: 466.52. Nimbolide is a limonoid tetranortriterpenoid shown to exhibit anti-malarial, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and anti-cancer activities. Nimbolide induces cell cycle arrest, DNA damage and apoptosis, and modulates autophagy in cancer cell lines. It inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and metastasis by inducing the excessive generation of ROS, reducing PI3K/Akt/mTOR and ERK signaling, and upregulating the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, caspase-3 and PARP. Nimbolide inhibits auto-ubiquitination of the E3 ligase RNF114 and p21 ubiquitination in vitro. This compound impairs proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. Nimbolide also induces apoptotic cell death in a Waldenstroms macroglobulinemia cell line (BCWM1) and inhibits tumor growth in a xenograft model of Waldenstroms macroglobulinemia. Nimbolide can be used for the development of Degraders that utilize RNF114 as an E3 ligase for Targeted Protein Degradation. Nimbolide exerts protective effects in complete Freund's adjuvant induced inflammatory arthritis via abrogation of STAT-3/NF-?B/Notch-1 signaling. Nimbolide suppresses high fat diet (HFD) induced obesity via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
MDL:
MFCD31924824
Molecular Formula:
C27H30O7
Molecular Weight:
466.52
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P301 + P312 + P330
Product Description:
Nimbolide is a limonoid tetranortriterpenoid shown to exhibit anti-malarial, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and anti-cancer activities. Nimbolide induces cell cycle arrest, DNA damage and apoptosis, and modulates autophagy in cancer cell lines. It inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and metastasis by inducing the excessive generation of ROS, reducing PI3K/Akt/mTOR and ERK signaling, and upregulating the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, caspase-3 and PARP. Nimbolide inhibits auto-ubiquitination of the E3 ligase RNF114 and p21 ubiquitination in vitro. This compound impairs proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. Nimbolide also induces apoptotic cell death in a Waldenstroms macroglobulinemia cell line (BCWM1) and inhibits tumor growth in a xenograft model of Waldenstroms macroglobulinemia. Nimbolide can be used for the development of Degraders that utilize RNF114 as an E3 ligase for Targeted Protein Degradation. Nimbolide exerts protective effects in complete Freund's adjuvant induced inflammatory arthritis via abrogation of STAT-3/NF-?B/Notch-1 signaling. Nimbolide suppresses high fat diet (HFD) induced obesity via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal Word:
Warning
SMILES:
CC1=C2[C@](CC1C3=COC=C3)([H])O[C@]([C@]2(C)[C@@H]4CC(OC)=O)([H])[C@@]5([H])C6[C@]4(C)C(C=C[C@@]6(C)C(O5)=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or DMF (10mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352211
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
[1] M.K. Roy, et al.; Phytother. Res. 21, 245 (2007) | [2] R.V. Priyadarsini, et al.; Free Radic. Res. 44, 624 (2010) | [3] S.C. Gupta, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 286, 1134 (2011) | [4] S. Babykutty, et al.; Mol. Carcinogen. 51, 475 (2012) | [5] K. Chitta, et al; Blood Cancer J. 4, 260 (2014) | [6] L.N. Bodduluru, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 28, 1026 (2014) (Review) | [7] R. Subramani, et al.; Sci. Rep. 6, 19819 (2016) | [8] P. Sakar, et al.; J. Med. Microbiol. 65, 1205 (2016) | [9] J. Sophia, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 9, 1087 (2018) | [10] N. Mahmoud, et al.; Oncotarget 9, 35762 (2018) | [11] J.N. Spradin, et al.; Nat. Chem. Biol. 15, 747 (2019) | [12] B. Tong, et al.; ACS Chem. Biol. 15, 1788 (2020) | [13] P. Anchi, et al.; Life Sci. 266, 118911 (2021) | [14] S. Nagini, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 64, 3560 (2021) (Review) | [15] L. Zhang, et al.; J. Oleo Sci. 71, 709 (2022) | [16] P.K. Jaiswara & A. Kumar; Environ. Toxicol. 37, 1445 (2022)