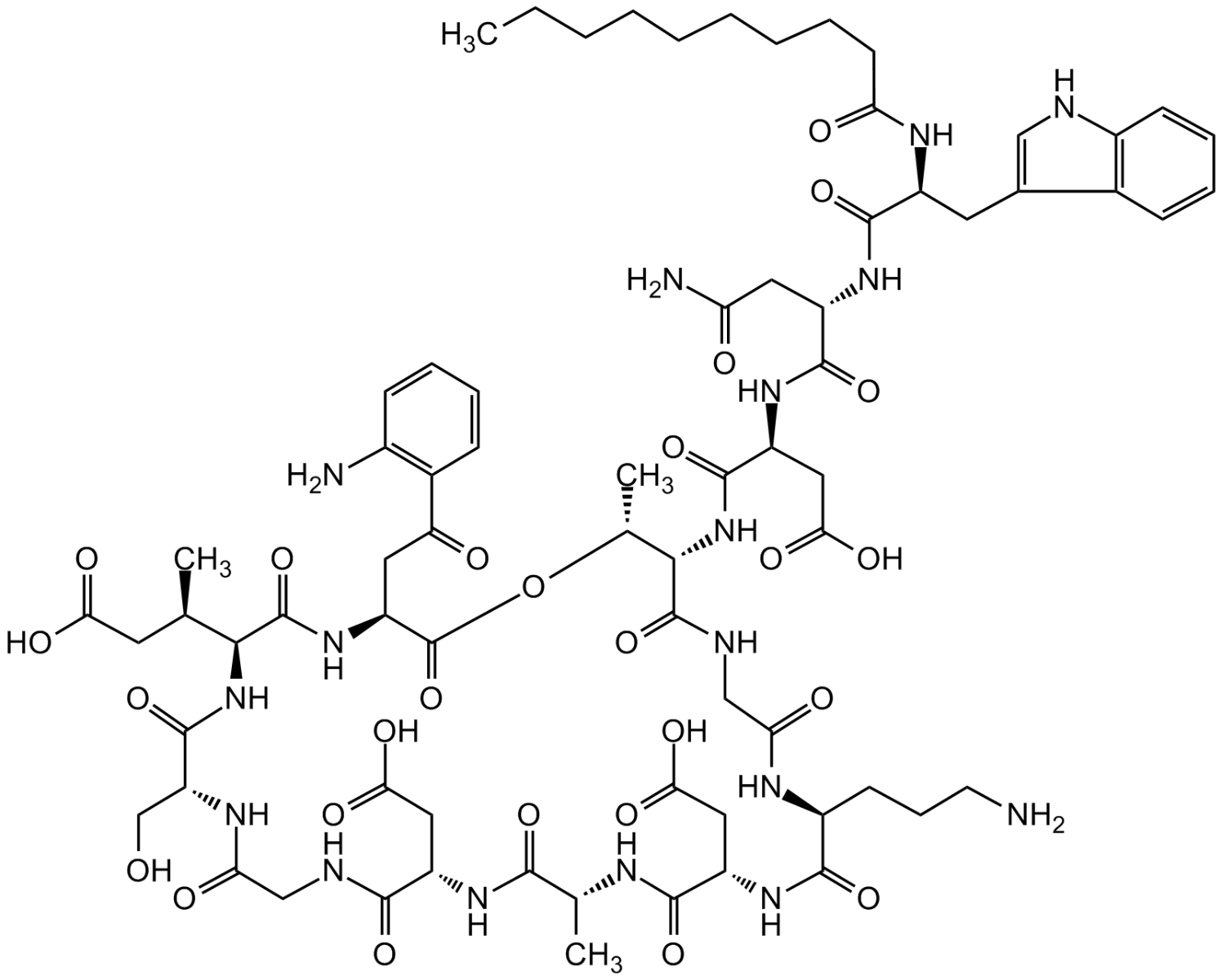
Daptomycin
Product Code: AG-CN2-0542
Product Group: Antibiotics and Other Antimicrobials
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0542-M025 | 25 mg | £65.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0542-M100 | 100 mg | £180.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
LY146032; Dapcin; Cubicin; Cidecin
Appearance:
Off-white to pale yellow powder.
CAS:
103060-53-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C72H101N17O26/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-22-53(93)81-44(25-38-31-76-42-20-15-13-17-39(38)42)66(108)84-45(27-52(75)92)67(109)86-48(30-59(102)103)68(110)89-61-37(4)115-72(114)49(26-51(91)40-18-12-14-19-41(40)74)87-71(113)60(35(2)24-56(96)97)88-69(111)50(34-90)82-55(95)32-77-63(105)46(28-57(98)99)83-62(104)36(3)79-65(107)47(29-58(100)101)85-64(106)43(21-16-23-73)80-54(94)33-78-70(61)112/h12-15,17-20,31,35-37,43-50,60-61,76,90H,5-11,16,21-30,32-34,73-74H2,1-4H3,(H2,75,92)(H,77,105)(H,78,112)(H,79,107)(H,80,94)(H,81,93)(H,82,95)(H,83,104)(H,84,108)(H,85,106)(H,86,109)(H,87,113)(H,88,111)(H,89,110)(H,96,97)(H,98,99)(H,100,101)(H,102,103)/t35-,36-,37-,43+,44+,45+,46+,47+,48+,49+,50-,60+,61+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
DOAKLVKFURWEDJ-RWDRXURGSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 103060-53-3. Formula: C72H101N17O26. MW: 1620.7. Daptomycin, a naturally occurring cyclic lipopeptide, is a calcium-dependent antibiotic. It exhibits potent bacteriocidal activity against most Gram-positive bacteria in vitro and in vivo, including antibiotic-resistant strains such as MRSA and VRE. Daptomycin disrupts the bacterial plasma membrane function, which results in membrane depolarization consequently leading to inhibition of protein, DNA and RNA synthesis, essential for cell division and cell wall synthesis.
MDL:
MFCD08282794
Molecular Formula:
C72H101N17O26
Molecular Weight:
1620.7
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Daptomycin, a naturally occurring cyclic lipopeptide, is a calcium-dependent antibiotic. It exhibits potent bacteriocidal activity against most Gram-positive bacteria in vitro and in vivo, including antibiotic-resistant strains such as MRSA and VRE. Daptomycin disrupts the bacterial plasma membrane function, which results in membrane depolarization consequently leading to inhibition of protein, DNA and RNA synthesis, essential for cell division and cell wall synthesis.
Product Line Areas NEW:
Antibiotic, Biochemicals, Natural Products, Cancer, Immunology, Inflammation
Product Type:
Chemical
Purity:
>95% (HPLC)
SMILES:
O=C(O[C@H](C)[C@H](NC([C@H](CC(O)=O)NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC(CCCCCCCCC)=O)CC1=CNC2=C1C=CC=C2)=O)CC(N)=O)=O)=O)C(NC3)=O)[C@H](CC(C4=C(N)C=CC=C4)=O)NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](CO)NC(CNC([C@H](CC(O)=O)NC([C@@H](C)NC([C@H](CC(O)=O)NC([C@@H](NC3=O)CCCN)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)[C@H](C)CC(O)=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (25mg/ml), DMSO (50mg/ml) or methanol (5mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20A°C.
References
In-vitro activity of vancomycin, teicoplanin, daptomycin, ramoplanin, MDL 62873 and other agents against staphylococci, enterococci and Clostridium difficile: A. Bartoloni, et al.; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 26, 627 (1990) | Development of daptomycin for Gram-positive infections: F.P. Tally & M.F. DeBruin; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 46, 523 (2000) | Structural transitions as determinants of the action of the calcium-dependent antibiotic daptomycin; D. Jung, et al.; Chem. Biol. 11, 949 (2004) | Daptomycin: A lipopeptide antibiotic for the treatment of serious Gram-positive infections: J.N. Steenbergen, et al.; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 55, 283 (2005) | The action mechanism of daptomycin: S.C. Taylor & M. Palmer; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 24, 6253 (2016) (Review) | More Than a Pore: A Current Perspective on the In Vivo Mode of Action of the Lipopeptide Antibiotic Daptomycin: D.A. Gray & M. Wenzel; Antibiotics 9, 17 (2020) (Review) | DAPTOMYCIN, its membrane-active mechanism vs. that of other antimicrobial peptides: H.W. Huang; Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1862, 183395 (2020) (Review) | The Antibiotic Peptide Daptomycin Functions by Reorganizing the Membrane: A. Pokorny & P.F. Almeida; J. Membr. Biol. 254, 97 (2021) (Review)