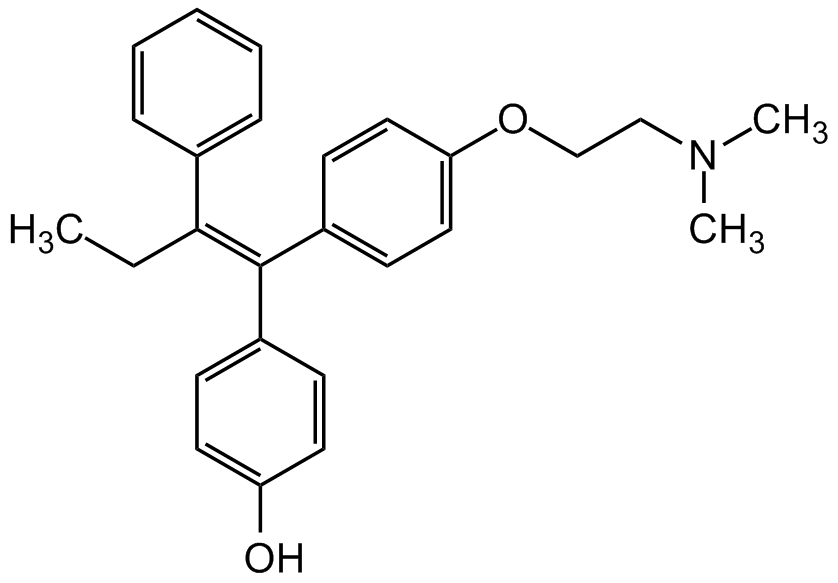
4-Hydroxytamoxifen
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-H0150-M050 | 50 mg | £150.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-H0150-M250 | 250 mg | £486.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short term: +20°C. Long term: +4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Afimoxifene; 4-OHT; cis/trans-4-Hydroxytamoxifen; (E/Z)-4-Hydroxytamoxifen; HTMX; 4-(1-[4-(Dimethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-2-phenyl-1-butenyl)phenol
Appearance:
White to yellow powder.
CAS:
68392-35-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07,GHS08
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302-H312-H332-H361
InChi:
InChI=1S/C26H29NO2/c1-4-25(20-8-6-5-7-9-20)26(21-10-14-23(28)15-11-21)22-12-16-24(17-13-22)29-19-18-27(2)3/h5-17,28H,4,18-19H2,1-3H3/b26-25-
InChiKey:
TXUZVZSFRXZGTL-QPLCGJKRSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 68392-35-8. Formula: C26H29NO2. MW: 387.51. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an active metabolite of the chemotherapeutic drug tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that acts as an agonist or antagonist in various tissues. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen acts as a tissue-selective agonist-antagonist of the estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an isoform-specific inhibitor of orphan estrogen-receptor-related (ERR) nuclear receptors beta and gamma. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic activity, inducing autophagy and vacuole formation as well as KRAS degradation in various cancer cell lines. In cardiac myocytes, 4-hydroxytamoxifen decreases Ca2+ amplitude, slowing relaxation and decreasing contractility. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen has also shown to be a potent inhibitor of the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT).
MDL:
MFCD00278780
Molecular Formula:
C26H29NO2
Molecular Weight:
387.51
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P280
Product Description:
4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an active metabolite of the chemotherapeutic drug tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that acts as an agonist or antagonist in various tissues. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen acts as a tissue-selective agonist-antagonist of the estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an isoform-specific inhibitor of orphan estrogen-receptor-related (ERR) nuclear receptors beta and gamma. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic activity, inducing autophagy and vacuole formation as well as KRAS degradation in various cancer cell lines. In cardiac myocytes, 4-hydroxytamoxifen decreases Ca2+ amplitude, slowing relaxation and decreasing contractility. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen has also shown to be a potent inhibitor of the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT).
Product Line Areas NEW:
Biochemicals, Cancer, Immunology
Product Type:
Chemical
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
CC/C(C1=CC=CC=C1)=C(C2=CC=C(O)C=C2)/C3=CC=C(OCCN(C)C)C=C3
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol or methanol (both 5mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4A°C.
References
[1] N. Terakawa, et al.; Cancer 61, 1312 (1988) | [2] H. Wiseman, et al.; FEBS Lett. 274, 107 (1990) | [3] G. Freiss, et al.; BBRC 173, 919 (1990) | [4] H. Wiseman, et al.; Biochem J. 292, 635 (1993) | [5] A.M. Davies, et al.; Biochem. Soc. Trans. 23, 439S (1995) | [6] S.T. Willard, et al.; Endocrine 14, 247 (2001) | [7] P. Coward, et al.; PNAS 98, 8880 (2001) | [8] G.B. Tremblay, et al.; Endocrinology 142, 4572 (2001) | [9] H.K. Crewe, et al.; Drug Metab. Dispos. 30, 869 (2002) | [10] C.M. Cardoso, et al.; Mitochondrion 1, 485 (2002) | [11] J.P. Monteiro, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 17, 629 (2003) | [12] Z. Desta, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 310, 1062 (2004) | [13] H. Seeger, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 36, 277 (2004) | [14] E.A. Ariazi & V.C. Jordan; Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 6, 203 (2006) (Review) | [15] M.L. Asp, et al.; PLoS One 8, e78768 (2013) | [16] L. Kohli, et al.; Cancer Res. 73, 4395 (2013) | [17] L. Duan, et al.; Cancer Lett. 353, 290 (2014)