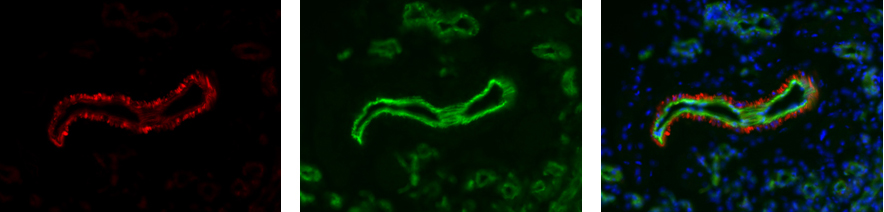
anti-Periostin mAb (blocking) (OC-20) (preservative free)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-20B-6000YPF-C100 | 100 ug | £390.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-20B-6000YPF-C500 | 500 ug | £1,510.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Mouse
Antibody Isotype: Mouse IgMkappa
Antibody Clonality: Monoclonal
Antibody Clone: OC-20
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species:
- Human
- Mouse
Applications:
- Blocking
- Functional Study
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
Shipping:
BLUE ICE
Storage:
Short Term Storage: +4°C. Long Term Storage: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Osteoblast-specific Factor 2; OSF-2; Postn
Concentration:
Lot dependent
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Sterile liquid. In 20mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH7.6 containing 150mM sodium chloride.
Handling Advice:
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Immunogen:
Recombinant fragments of human periostin.
Long Description:
Monoclonal Antibody. Recognizes human and mouse periostin. Detects the FAS1-2 domain of periostin at a new binding site for the integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5. Isotype: Mouse IgMkappa. Clone: OC-20. Applications: FUNC (Blocking), ICC. Liquid. In 20mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH7.6 containing 150mM sodium chloride. Periostin is a 90-kDa matricellular protein that consists of a typical signal sequence, followed by a cysteine-rich region, an EMI domain (protein-protein interactions), four tandem fasciclin-like domains that are responsible for integrin binding, and a C-terminal region. Periostin was originally isolated as an osteoblast-specific factor that functions as a cell adhesion molecule for pre-osteoblasts and in osteoblast recruitment, attachment and spreading. Periostin is also involved in many fundamental biological processes such as cell proliferation, cell invasion and angiogenesis. Periostin expression is increased by both transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). Changes in periostin expression are commonly detected in various cancers and pre-cancerous conditions, and periostin may be involved in regulating cancer cell activities that contribute to tumorigenesis, cancer progression and metastasis. Periostin has shown to be involved in many aspects of allergic inflammation, such as eosinophil recruitment, airway remodeling, development of a Th2 phenotype and increased expression of inflammatory mediators. It is evaluated as a biomarker for bronchial asthma and airway inflammation.
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Periostin is a 90-kDa matricellular protein that consists of a typical signal sequence, followed by a cysteine-rich region, an EMI domain (protein-protein interactions), four tandem fasciclin-like domains that are responsible for integrin binding, and a C-terminal region. Periostin was originally isolated as an osteoblast-specific factor that functions as a cell adhesion molecule for pre-osteoblasts and in osteoblast recruitment, attachment and spreading. Periostin is also involved in many fundamental biological processes such as cell proliferation, cell invasion and angiogenesis. Periostin expression is increased by both transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). Changes in periostin expression are commonly detected in various cancers and pre-cancerous conditions, and periostin may be involved in regulating cancer cell activities that contribute to tumorigenesis, cancer progression and metastasis. Periostin has shown to be involved in many aspects of allergic inflammation, such as eosinophil recruitment, airway remodeling, development of a Th2 phenotype and increased expression of inflammatory mediators. It is evaluated as a biomarker for bronchial asthma and airway inflammation.
Product Line Areas NEW:
Cancer, Immunology, Inflammation, Antibodies
Purity:
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Source / Host:
Purified from concentrated hybridoma tissue culture supernatant.
Specificity:
Recognizes human and mouse periostin. Detects the FAS1-2 domain of periostin at a new binding site for the integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Primary Antibodies
UNSPSC Number:
12352203
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Identification of a novel cell binding site of periostin involved in tumour growth: P. Orecchia, et al.; Eur. J. Cancer 47, 2221 (2011) | Periostin promotes fibrosis and predicts progression in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: P.K. Naik, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 303, L1046 (2012) | Periostin is required for maximal airways inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in mice: J.K. Bentley, et al.; J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 134, 1433 (2014) | Periostin is a novel therapeutic target that predicts and regulates glioma malignancy: A.M. Mikheev, et al.; Neuro Oncol. 17, 372 (2015) | Periostin: its role in asthma and its potential as a diagnostic or therapeutic target: W. Li, et al.; Resp. Res. 16, 57 (2015) | Imaging of secreted extracellular periostin, an important marker of invasion in the tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer: P. Heidari, et al.; J. Nucl. Med. 56, 1246 (2015) | Single-cell RNA-seq reveals fibroblast heterogeneity and increased mesenchymal fibroblasts in human fibrotic skin diseases: Ch.Ch. Deng, et al.; Nat. Comm. 12, 3709 (2021) | Periostin secreted by activated fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis promotes tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer: H. Yamato, et al.; Nat. Sci. Rep. 11, 21114 (2021)