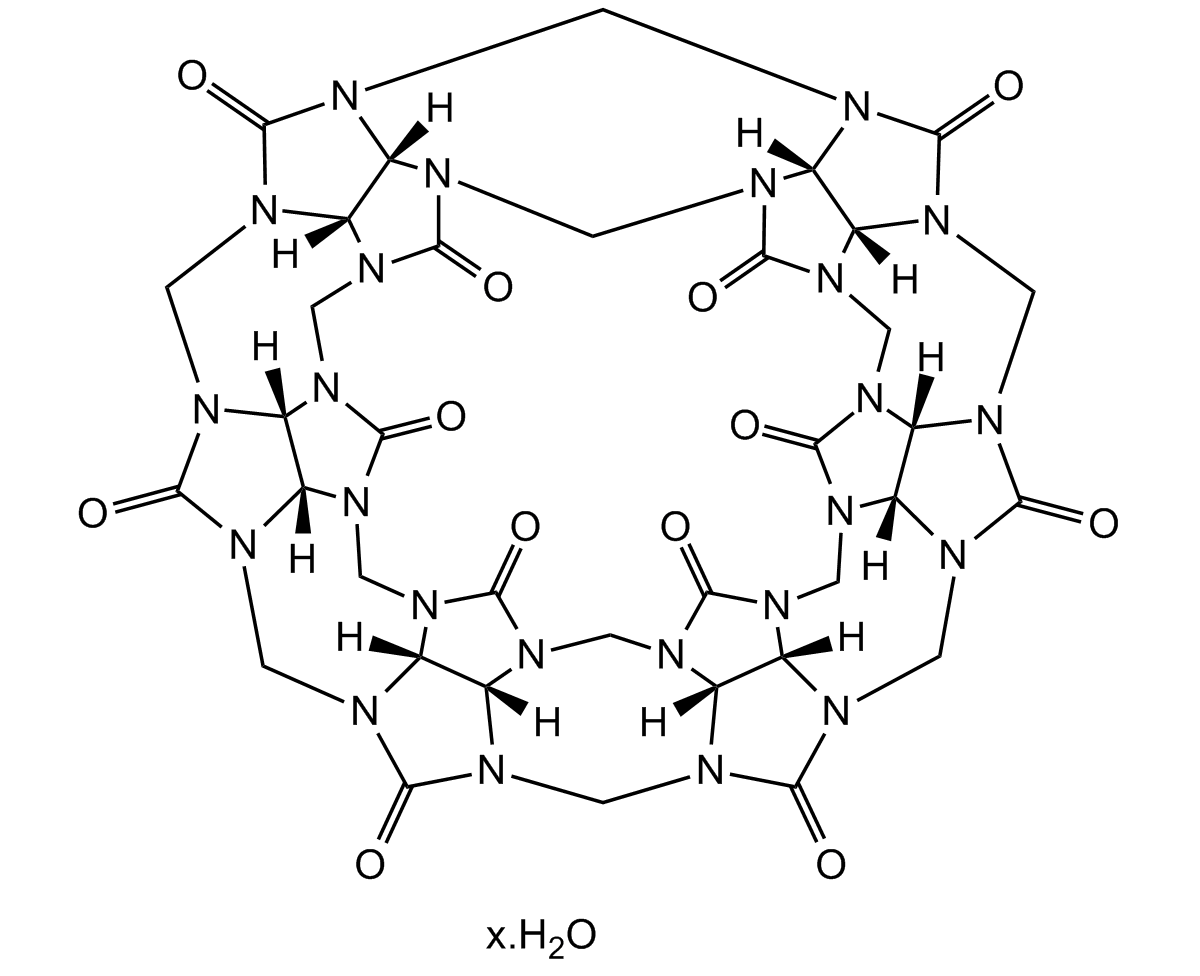
Cucurbit[6]uril hydrate
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0239-G001 | 1 g | £92.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short term storage:+20°C. Long term storage:+20°C.
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Cucurbituril
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
80262-44-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C36H36N24O12/c61-25-37-1-38-14-16-42(26(38)62)4-46-18-20-50(30(46)66)8-54-22-24-58(34(54)70)11-57-23-21-53(33(57)69)7-49-19-17-45(29(49)65)3-41(25)15-13(37)39-2-40(14)28(64)44(16)6-48(18)32(68)52(20)10-56(22)36(72)60(24)12-59(23)35(71)55(21)9-51(19)31(67)47(17)5-43(15)27(39)63/h13-24H,1-12H2/t13-,14+,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20-,21-,22+,23+,24-
InChiKey:
MSBXTPRURXJCPF-DQWIULQBSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 80262-44-8. Formula: C36H36N24O12. MW: 996.84. Cucurbit[6]uril hydrate belongs to the Cucurbit[n]uril (CB[n], n = 5-10) family of macrocyclic compounds comprising n glycoluril units, self-assembled from an acid-catalyzed condensation reaction of glycoluril and formaldehyde. The pumpkin-shaped CB molecules have a hydrophobic cavity and two identical carbonyllaced portals. While the hydrophobic interior provides a potential inclusion site for nonpolar molecules, the polar ureido carbonyl groups at the portals allow CB[n] to bind ions and molecules through charge-dipole and hydrogen bonding interactions. The unique structure and recognition properties make CB[n] attractive not only as a synthetic receptor but also as a building block for the construction of supramolecular architectures. In the wide area of supramolecular chemistry, cucurbit[n]urils (CBn) present themselves as molecular containers, able to form stable complexes with various guests, including drug molecules, amino acids and peptides, saccharides, dyes, hydrocarbons, perfluorinated hydrocarbons, and even high molecular weight guests such as proteins (e.g. human insulin). Furthermore, a direct functionalization method of CB[n] allowed the synthesis of a wide variety of tailor-made CB derivatives to study many applications. Ion channels, vesicles, polymers, nanomaterials, ion selective electrodes incorporating CB[n], and CB-immobilized solid surfaces and silica gel have been reported. Numerous other applications are being explored.
MDL:
MFCD01310281
Molecular Formula:
C36H36N24O12
Molecular Weight:
996.84
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Cucurbit[6]uril hydrate belongs to the Cucurbit[n]uril (CB[n], n = 5-10) family of macrocyclic compounds comprising n glycoluril units, self-assembled from an acid-catalyzed condensation reaction of glycoluril and formaldehyde. The pumpkin-shaped CB molecules have a hydrophobic cavity and two identical carbonyllaced portals. While the hydrophobic interior provides a potential inclusion site for nonpolar molecules, the polar ureido carbonyl groups at the portals allow CB[n] to bind ions and molecules through charge-dipole and hydrogen bonding interactions. The unique structure and recognition properties make CB[n] attractive not only as a synthetic receptor but also as a building block for the construction of supramolecular architectures. In the wide area of supramolecular chemistry, cucurbit[n]urils (CBn) present themselves as molecular containers, able to form stable complexes with various guests, including drug molecules, amino acids and peptides, saccharides, dyes, hydrocarbons, perfluorinated hydrocarbons, and even high molecular weight guests such as proteins (e.g. human insulin). Furthermore, a direct functionalization method of CB[n] allowed the synthesis of a wide variety of tailor-made CB derivatives to study many applications. Ion channels, vesicles, polymers, nanomaterials, ion selective electrodes incorporating CB[n], and CB-immobilized solid surfaces and silica gel have been reported. Numerous other applications are being explored.
Purity:
>95% (N)
SMILES:
O=C(N(C1)[C@@]2([H])N3CN4[C@@]5([H])N1C(N(CN6[C@]7([H])N8C(N(C9)[C@]7([H])N(C%10)C6=O)=O)[C@@]5([H])N(C8)C4=O)=O)N(CN%11[C@@]%12([H])N%13C(N(C%14)[C@@]%12([H])N(CN%15[C@@]%16([H])N%14C(N(C%17)[C@@]%16([H])N(CN%18[C@@]%19([H])N%17C(N9[C@@]%19([H])N%10C%18=O)=O)C%15=O)=O)C%11=O)=O)[C@]2([H])N(C%13)C3=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Very slightly soluble in water or DMSO.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) W.L. Mock & N.-Y. Shih; J. Org. Chem. 48, 3619 (1983) | (2) J. Zhao, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40, 4233 (2001) | (3) K. Kim; Chem. Soc. Rev. 31, 96 (2002) | (4) Y.-B. Lim; et al.; Bioconjugate Chem. 13, 1181 (2002) | (5) J.W. Lee, et al.; Acc. Chem. Res. 36, 621 (2003) | (6) S.Y. Jon, et al.; JACS 125, 10186 (2003) | (7) J. Lagona, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 4844 (2005) | (8) K. Kim, et al.; Chem. Soc. Rev. 36, 267 (2007) | (9) D. Kim, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 3471 (2007) | (10) E. Kim, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 4405 (2010) | (11) K.I. Assaf & W.M. Nau; Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 394 (2015) | (12) D. Das, et al.; Front. Chem. 7, 619 (2019) | (13) R. Gao, et al.; Molecules 28, 3566 (2023) | (14) S. Shukla, et al.; ASC Appl. Bio. Mater. 6, 2089 (2023)