Anti-Human Apoptosis Inducing Factor (NT) (AIF)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-A153-20ug | 20 ug | £199.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-A153-0.1mg | 0.1 mg | £591.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Immunohistochemistry- Paraffin Embedded (IHC-P)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles.
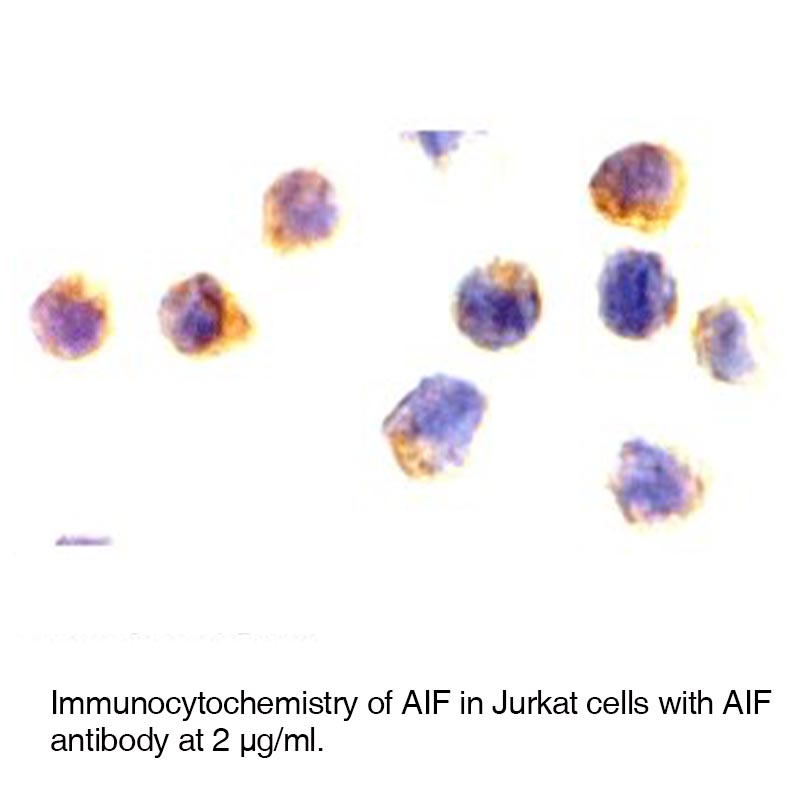
Images
Further Information
Concentration:
0.5 mg/ml
Conjugate/Tag/Label:
Purified No Carrier Protein
Format:
This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative.
Formulation:
This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative.
Immunogen:
PN:A172
Long Description:
Apoptosis is characterized by several morphological nuclear changes including chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation. These changes are triggered by the activation of members of caspase family, caspase activated DNase, and several novel proteins.1 A novel gene, the product of which causes chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation, was recently identified, cloned, and designated apoptosis inducing factor (AIF).2 Like the critical molecules, cytochrome c and caspase-9, in apoptosis, AIF localizes in mitochondria. AIF translocates to the nucleus when apoptosis is induced and induces mitochondria to release the apoptogenic proteins cytochrome c and caspase-9. AIF induces chromatin condensation and large scale DNA fragmentation, which are the hallmarks of apoptosis, of the isolated nucleus and the nucleus in live cells by microinjection and apoptosis stimuli.2,3 AIF is highly conserved between human and mouse and widely expressed.2
Target:
Apopotosis Inducing Factor
References
1. Zamzami, N. and Kroemer, G. (1999) Nature 401:127-8 2. Susin, SA. et al. (1999) Nature 397:441-6 3. Daugas, E. et al. (2000) FASEB J 14:729-39