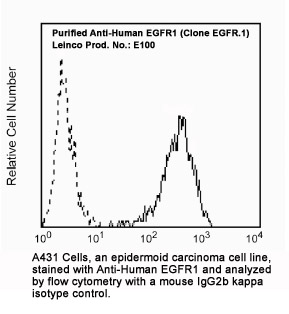
Anti-Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-E100-0.25mg | 0.25 mg | £315.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Mouse
Antibody Isotype: IgG2b κ
Antibody Clonality: Monoclonal
Antibody Clone: EGFR.1
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Application: Flow Cytometry
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
This purified antibody is stable when stored at 2-8°C. Do not freeze.
Images
Further Information
Concentration:
0.5 mg/ml
Conjugate/Tag/Label:
Purified
Format:
This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4, 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide as a preservative.
Formulation:
This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4, 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide as a preservative.
Immunogen:
A431 cultured cells
Long Description:
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is the cell-surface receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF-family) of extracellular protein ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR (ErbB-1), HER2/c-neu (ErbB-2), Her 3 (ErbB-3) and Her 4 (ErbB-4). Mutations affecting EGFR expression or activity could result in cancer. EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) exists on the cell surface and is activated by binding of its specific ligands, including epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor α (TGFα) (note, a full list of the ligands able to activate EGFR and other members of the ErbB family is given in the ErbB article). ErbB2 has no known direct activating ligand, and may be in an activated state constitutively or become active upon heterodimerization with other family members such as EGFR. Upon activation by its growth factor ligands, EGFR undergoes a transition from an inactive monomeric form to an active homodimer - although there is some evidence that preformed inactive dimers may also exist before ligand binding. In addition to forming homodimers after ligand binding, EGFR may pair with another member of the ErbB receptor family, such as ErbB2/Her2/neu, to create an activated heterodimer. There is also evidence to suggest that clusters of activated EGFRs form, although it remains unclear whether this clustering is important for activation itself or occurs subsequent to activation of individual dimers.
Target:
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
References
1. Berger, SM. et al. (1987) J. of Pathology 152:297 2. Downward, J. et al. (1984) Nature 311:483 3. Gullick, WJ. et al. (1985) EMBO J. 4:2869 4. Gullick, WJ. et al. (1986) Cancer Research 46:285 5. Gullick, WJ. et al. (1991) Br. Med. Bulletin 47:87