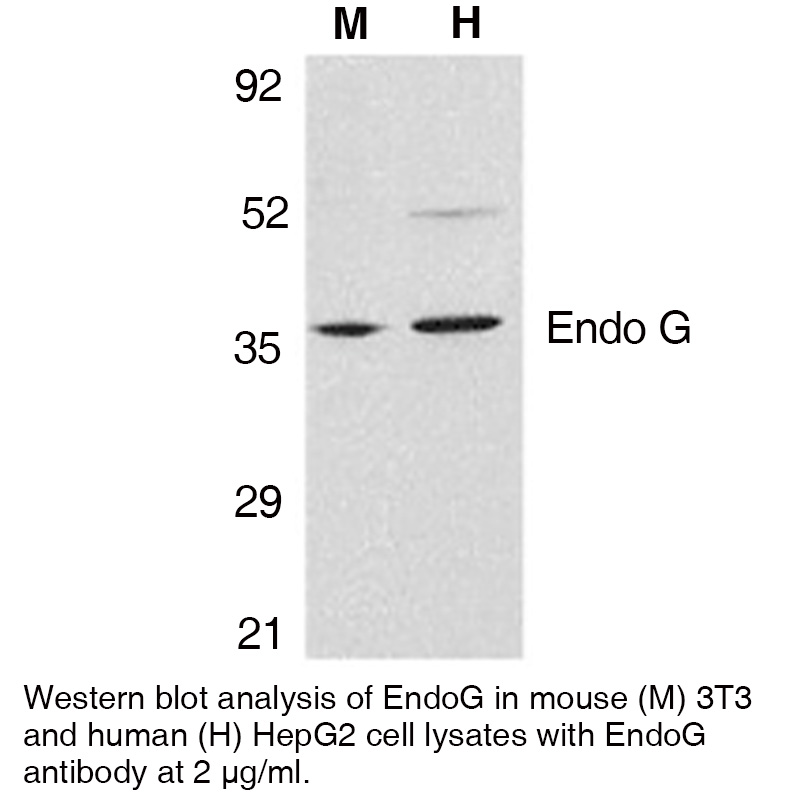
Anti-Human EndoG
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-E132-20ug | 20 ug | £199.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-E132-0.1mg | 0.1 mg | £591.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Immunohistochemistry- Paraffin Embedded (IHC-P)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles.
Images
Further Information
Concentration:
0.5 mg/ml
Conjugate/Tag/Label:
Purified No Carrier Protein
Format:
This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative.
Formulation:
This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative.
Immunogen:
PN:E133
Long Description:
The fragmentation of nuclear DNA is a hallmark of apoptotic cell death. The activities of caspase and nuclease are involved in the DNA fragmentation. Caspase-activated deoxyribonuclease (CAD), also termed DNA fragmentation factor (DFF40), is one such nuclease, and is capable of inducing DNA fragmentation and chromatin condensation after cleavage by caspase-3 of its inhibitor ICAD/DFF45. Caspase and CAD independent DNA fragmentation also exists. Recent studies demonstrated that another nuclease, endonuclease G (endoG), is specifically activated by apoptotic stimuli and is able to induce nucleosomal fragmentation of DNA independently of caspase and DFF/CAD.1,2 EndoG is a mitochondrion-specific nuclease that translocates to the nucleus and cleaves chromatin DNA during apoptosis. The homologue of mammalian EndoG is the first mitochondrial protein identified to be involved in apoptosis in C. elegans.2 EndooG also cleaves DNA in vitro.4
Target:
EndoG
References
1. Li, LY. et al.(2001) Nature. 412(6842):95-9. 2. Parrish, J. et al. (2001) Nature. 412(6842):90-4. 3. Hengartner, MO. et al. (2001) Nature. 412(6842):27-9. 4. Widlak, P. et al. (2001) J Biol Chem. 276(51):48404-9.