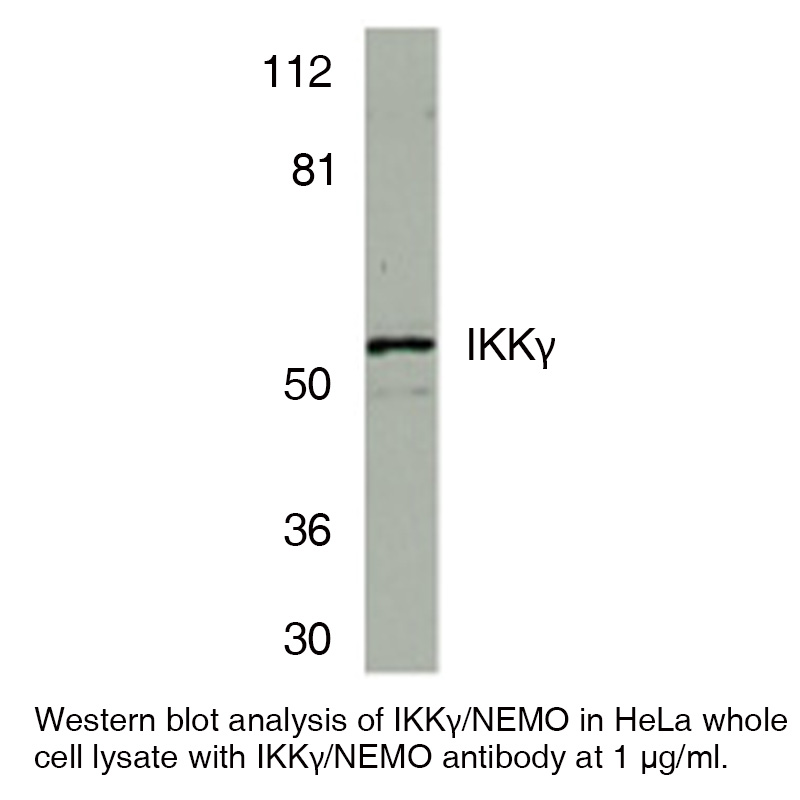
Anti-Human I-Kappa-B Kinase Gamma (NT) (IKKγ)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-I-304-20ug | 20 ug | £199.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-I-304-0.1mg | 0.1 mg | £591.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Immunohistochemistry- Paraffin Embedded (IHC-P)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles.
Images
Further Information
Concentration:
0.5 mg/ml
Conjugate/Tag/Label:
Purified No Carrier Protein
Format:
This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative.
Formulation:
This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative.
Immunogen:
PN:I-318
Long Description:
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a ubiquitous transcription factor and an essential mediator of gene expression during activation of immune and inflammatory responses. NF-κB mediates the expression of a great variety of genes in response to extracellular stimuli. NF-κB is associated with IkB proteins in the cell cytoplasm, which inhibit NF-κB activity. The IkB kinase (IKKα and IKKβ) phosphorylates IkB and mediates NF-κB activation. A novel molecule in the IKK complex was recently identified and termed IKKγ/NEMO/FIP3/IKKAP1.1-4 IKKg interacts with IKKβ and is required for the activation of IKK complex and NF-κB by LPS, PMA, TNF, and IL-1 stimulation.1-4 FIP3 was also shown to bind to RIP and NIK and to mediate TNF-induced NF-κB activation.3
Target:
I-Kappa-B Kinase Gamma
References
1. Rothwarf, DM. et al. (1998) Nature 395(6699):297 2. Yamaoka, S. et al. (1998) Cell 93(7):1231 3. Li, Y. et al. (1999) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96(3):1042 4. Mercurio, F. et al. (1999) Mol. Cell Biol. 19(2):1526