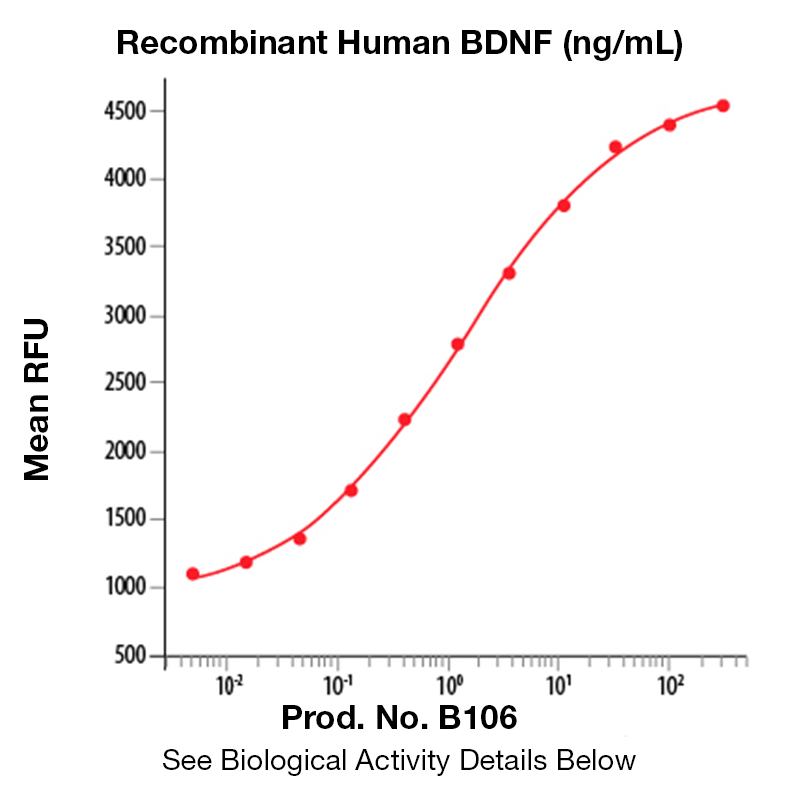
Recombinant Human Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-B106-5ug | 5 ug | £534.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-B106-50ug | 50 ug | £1,126.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-B106-10ug | 10 ug | £8,386.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Human
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
This lyophilized protein is stable for six to twelve months when stored desiccated at -20°C to -70°C. After aseptic reconstitution this protein may be stored at 2°C to 8°C for one month or at -20°C to -70°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. See Product Insert for exact lot specific storage instructions.
Images
Further Information
Format:
This recombinant protein was 0.2 um filtered and lyophilized from a filtered solution in 100mM Sodium Citrate and 300 mM NaCl, pH 3.0.
Formulation:
This recombinant protein was 0.2 um filtered and lyophilized from a filtered solution in 100mM Sodium Citrate and 300 mM NaCl, pH 3.0.
Long Description:
Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF), also known as MGC34632, is a member of the NGF family of neurotrophic growth factors that includes NGF, NT-3, and NT-4/5. Like other members of this family, BDNF supports neuron proliferation and survival (1). It acts on certain neurons of the central and peripheral nervous systems, helping to support the survival of existing neurons and encourage the growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses. In the brain, BDNF is active in the hippocampus, cortex, and basal forebrain, areas vital to learning, memory and higher thinking (2). Despite its name, BDNF is actually found in a range of tissue and cell types, not just in the brain. It is also expressed in the retina, the CNS, motor neurons, the kidneys and the prostate. BDNF binds at least two receptors on the surface of cells which are capable of responding to this growth factor, TrkB and the LNGFR (3). Expression of BDNF is reduced in both Alzheimer's and Huntington disease patients (4-5). In addition, functional studies showed that age-associated changes in BDNF-mediated pathways can enhance inflammation and increase myocardial injury after myocardial infarction in the aging heart (6). Various studies have shown possible links between BDNF and other conditions, such as depression, schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, Rett syndrome, dementia, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, epilepsy and eczema.
NCBI Gene:
627
Purity:
>97% by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by silver stain.
Target:
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
References
1. Acheson, A. et al. (1995) Nature 374:450
2. Yamada, K. et al. (2003) J. Pharmacol. Sci. 91 :267
3. Patapoutian, A. et al. (2001) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11:272
4. Zuccato, C. et al. (2009) Nat. Rev. Neurol. 5:311
5. Zajac, MS. et al. (2009) Hippocampus 20:621
6. Cai, D. et al. (2006) Physiol. Genomics 24:191