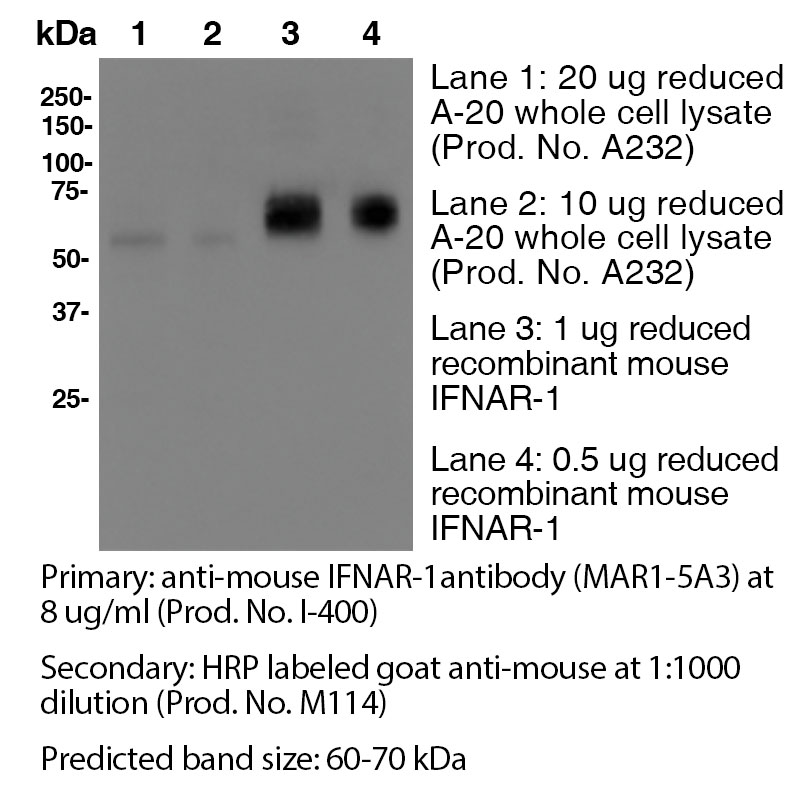
Anti-Mouse IFNAR-1 (Clone MAR1-5A3) - Purified
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-I-400-25ug | 25 ug | £141.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-I-400-100ug | 100 ug | £209.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-I-400-200ug | 200 ug | £310.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Mouse
Antibody Isotype: IgG1
Antibody Clonality: Monoclonal
Antibody Clone: MAR1-5A3
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Mouse
Applications:
- Blocking
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Flow Cytometry
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
2-8°C
Storage:
This purified antibody is stable when stored at 2-8°C. Do not freeze.
Images
Further Information
Antigen Distribution:
IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 are coexpressed on nearly all cells.
Concentration:
0.5 mg/ml
Conjugate/Tag/Label:
Purified
Format:
This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4, 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide as a preservative.
Formulation:
This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4, 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide as a preservative.
Immunogen:
This antibody was produced by In vivo genetic immunization of IFNAR1 knockout mice with a plasmid encoding the extracellular domain of murine IFNAR1.
Long Description:
IFNAR1 is a type I membrane protein, that in conjunction with IFNAR2, makes up the heterodimeric receptor that binds all type I IFNs, which includes IFN α and β. Binding and activation of the receptor stimulates Janus protein kinases, which leads to the phosphorylation of several other proteins, namely STAT1 and STAT2. IFNAR1 has also been shown to interact with PRMT1 and Tyrosine kinase 2. Type I IFNs are a family of cytokines that have been shown to promote anti-viral, anti-microbial, anti-tumor and autoimmune responses In vivo.
NCBI Gene:
15975
Target:
IFNAR1
References
1. Sheehan, K. C. F. et al. (2006) JICR 26(11):804
2. Dunn, G. P. et al. (2005) Nat. Immunol. 6(7):722
3. Fenner, J. E. et al. (2006) Nat. Immunol. 7(1):33