Anti-SLC40A1 (FPN1) (Human) pAb
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-BMP033 | 50 uL | £323.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Isotype: IgG
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Flow Cytometry
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternative Names:
ferroportin 1
Applications:
WB - 1:1000 (chemiluminescence detection system) FCM - 1:1000 ICC - 1:1000 IHC - 1:5000 (Heat treatment required for paraffin)
Background:
SLC40A1, also known as ferroportin
1, belongs to the iron-regulated transporter family and
absorbs iron from the diet into the bloodstream through the
small intestine. The absorbed iron binds to transferrin in the
blood and is then carried to tissues and organs throughout
the body. SLC40A1 also transports iron out of
reticuloendothelial cells, which are phagocytic immune
cells present in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
Mutations in the
SLC40A1
gene cause hemochromatosis,
which is characterized by impaired iron regulation and
disorders associated with ir
on deficiency or overload.
Formulation:
50 ul volume of PBS containing50% glycerol, pH 7.2. No preservative is contained.
Gene IDs:
Human: 30061 Mouse: 53945
Immunogen Translated:
Synthetic peptide derived from human SLC40A1
Reactivity:
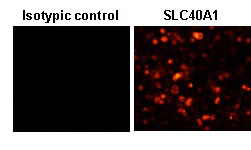
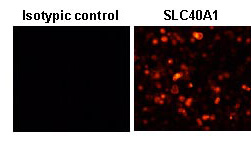
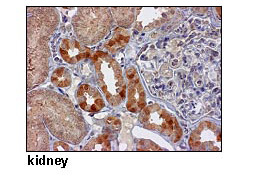
This antibody can be used to stain
endogenous antigen in paraffin embedded human tissues
including kidney by Immunohistochemistry. The reactivity
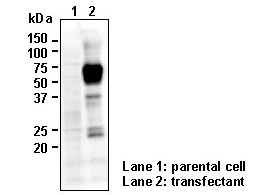
has been confirmed by Western blotting,
Immunocytochemistry, and intr
acellular Flow cytometry to
detect the full length of human SLC40A1 transiently
expressed in HEK 293T cells.
Shelf Life:
1 year
Source:
This antibody was affinity purified from rabbit
serum. The rabbit was immunized with a synthetic peptide
derived from human SLC40A1.
Target:
SLC40A1
References
?1) Zohn, I. E., et al., Blood 109, 4174-4180 (2007)
2) Donovan, A., et al., Cell Metab. 1, 191-200 (2005)
3) Domenico, I. D., et al., PNAS 102, 8955-8960 (2005)
4) Montosi, G., et al., J. Clin. Invest. 108, 619-623 (2001)
5) Donovan, A., et al., Nature 403, 776-781 (2000)
6) McKie, A. T., et al., Mol. Cell 5, 299-309 (2000)