Anti-SLC6A14 (ATB0+) (Human) pAb
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-BMP052 | 50 uL | £541.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Isotype: IgG
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Flow Cytometry
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternative Names:
ATB0+
Applications:
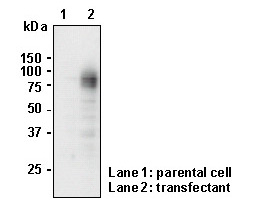
WB - 1:1000 (chemiluminescence detection system) FCM - 1:1000 ICC - 1:1000 IHC - 1:5000 (Heat treatment required for paraffin)
Background:
SLC6A14, also known as ATB0+, is a member of the Na+ - and Cl- - dependent neurotransmitter transporter family, and is highly expressed in the lung, fetal lung, trachea, and salivary gland. SLC6A14 transports both neutral and cationic amino acids, and has about 60% amino acid similarity with the glycine transporters GLYT1 and GLYT2. The blockade of ATB0+ in cancer cell lines is associated with cell cycle arrest, indicating the potential of ATB0+ as a drug target in cancer chemotherapy.
Formulation:
50 ul volume of PBS containing50% glycerol, pH 7.2. No preservative is contained.
Gene IDs:
Human: 11254 Mouse: 56774
Immunogen Translated:
Synthetic peptide derived from human SLC6A14
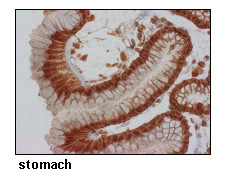
Reactivity:
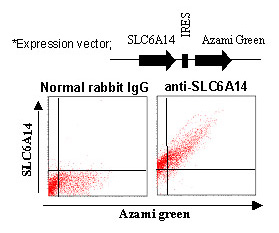
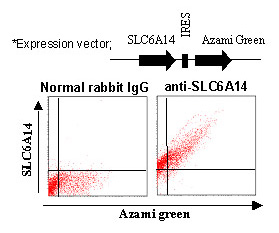
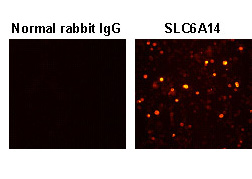
This antibody can be used to stain endogenous antigen in paraffin embedded human tissues including stomach by Immunohistochemistry. The reactivity has been confirmed by Western blotting, Immunocytochemistry and Flow cytometry to detect the full length of human SLC6A14 transiently expressed in HEK 293T cells.
Shelf Life:
1 year
Source:
This antibody was affinity purified from rabbit serum. The rabbit was immunized with a synthetic peptide derived from human SLC6A14.
Target:
SLC6A14
References
1)
Anderson, C. M. H., et al., J. Physiol. 586, 4061-4067 (2008)
2)
Karunakaran, S., et al., Biochem. J. 414, 343-355 (2008)
3)
Sloan, J. L., and Mager, S., J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23740-23745 (1999)