Anti-SLC1A2 (EAAT2) (Human) pAb
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-BMP069 | 100 ul | £323.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Isotype: IgG
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Flow Cytometry
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Applications:
FCM - 1:500 ICC - 1:500 IHC - 1:2500 (Heat treatment required for paraffin)
Background:
Members of the solute carrier family 1 are classified as high-affinity glutamate and neutral amino acid transporters. These are also referred to as excitatory amino acid transporters, which regulate glutamatergic signal transmission by clearing excess glutamate after synaptic release in the central nervous system. SLC1A2/EAAT2 is predominantly located on the astroglia in the brain and is believed to act as a glial-specific glutamate transporter. Lethal seizures and increased susceptibility to acute cortical injury have been observed in mice with disrupted slc1a2 gene. In humans, a severe decrease in the expression levels of SLC1A2/EAAT2 is noted in the brain of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Formulation:
100 ul volume of PBS containing 50% glycerol, pH 7.2. No preservative is contained.
Gene IDs:
Human: 6506 Mouse: 20511
Immunogen Translated:
Synthetic peptide derived from human SLC1A2
Reactivity:
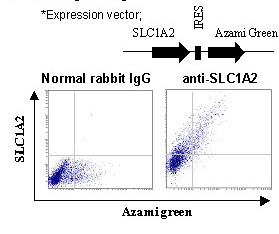
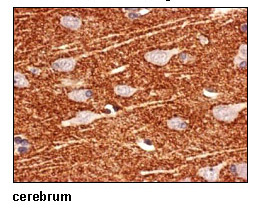
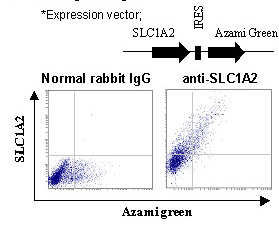
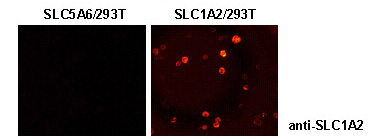
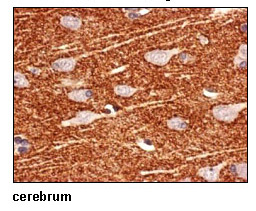
This antibody can be used to stain endogenous antigen in paraffin embedded human tissues including the cerebrum by Immunohistochemistry. The reactivity has been confirmed by Immunocytochemistry and intracellular Flow cytometry to detect the full length of human SLC1A2 transiently expressed in HEK 293T cells.
Shelf Life:
1 year
Source:
This antibody was affinity purified from rabbit serum. The rabbit was immunized with a synthetic peptide derived from human SLC1A2.
Target:
SLC1A2/EAAT2
References
1)
Mallolas, J., et al., J. Exp. Med. 203, 711-717 (2006)
2)
Su, Z., et al., PNAS 100, 1955-1960 (2003)
3)
Trotti, D., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 276, 576-582 (2001)
4)
Tanaka, K., et al., Science 276, 1699-1702 (1997)
5)
Shashidharan, P., et al., Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1191, 393-396 (1994)
6)
Rothstein, J. D., et al., Neuron 13, 713-725 (1994)
7)
Krishnan, S. N., et al., Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 19, 219 (1993)