Anti-Flavocytochrome b558 (Human) mAb-PE
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-D162-5 | 50 Tests | £328.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Mouse
Antibody Isotype: IgG1
Antibody Clonality: Monoclonal
Antibody Clone: 7D5
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
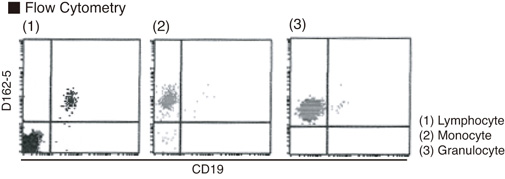
Application: Flow Cytometry
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Applications:
FCM - 20 uL (ready for use)
Background:
The NADPH oxidase is a
multicomponent enzyme that transfers electrons from
NADPH to O
2
to generate superoxide (O
2
-
), a key part of
the phagocytic or neutrophilic respiratory burst response.
Flavocytochrome b
558
is the catalytic component of the
phagocyte NADPH oxidase. It is a transmembrane
heterodimer composed of a large glycoprotein, gp91
phox
(PHagocyte OXidase) and a smaller protein, p22
phox
.
Upon cell stimulation, flavocytochrome b
558
assembles
with p67
phox
, p47
phox
, and the GTP-binding protein Rac
and becomes activated to generate O
2
-
. Mutations in
gp91
phox
, p22
phox
, or other components of the NADPH
oxidase can result in chronic granulomatous disease,
which is associated with
significant morbidity and
mortality due to a predisposition to recurrent bacterial and
fungal infections.
Conjugate:
PE
Gene IDs:
Human: 1535, 1536 Mouse: 13057
Immunogen Translated:
Rich fraction of human cytochrome b
Reactivity:
This antibody recognizes the
extracellular peptide portion of primate gp91
phox
of the
human Flavocytochrome b
558
on Flow cytometry.
Shelf Life:
1 year
Source:
This antibody was purified from hybridoma
(clone 7D5) supernatant using protein A agarose. This
hybridoma was established by fusion of mouse myeloma
cell Sp2/0 with Balb/c mouse splenocyte immunized with
the human cytochrome b rich fraction.
Target:
Flavocytochrome b558
References
Li, X. J., et al., J. Leukoc. Biol. 10.1189/Jlb.0905541. (2006)
Reumaux, D., et al., J. Leukoc. Biol. 10.1189/Jlb.0304144. (2006)
Taylor, R. M., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 281, 37045-37056 (2006)
Zhu, Y., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 281, 30336-30346 (2006)
Li, X. J., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 280, 14962-14973 (2005)
Allen, L-A. H., et al., J. Immunol. 174, 3658-3667 (2005)
Carlyon, J. A., et al., Infect. Immun. 72, 4772-4783 (2004)
Brenner, S., et al., Blood 102, 2789-2797 (2003)
Burritt, J. B., et al., J. Immunol. 170, 6082-6089 (2003)
Carlyon, J. A., et al., J. Immunol. 169, 7009-7018 (2002)
Morgan, D., et al., J. Gen. Physiol. 119, 571-580 (2002)
Yamauchi, A., et al., Microbiol. Immunol. 45, 249-57 (2001)
Burritt, J. B., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2053-2061 (2001)
Yu, L., et al., Blood 94, 2497-2504 (1999)
Yu, L., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA95, 7993?7998 (1998)
Radeke, H. H., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 266, 21025-21029 (1991)
Verhoeven, A., et al., Blood 73, 1686-1694 (1989)
Nakamura, M., et al., Blood 69,1404-1408 (1987)